Personalized Pharmacotherapy for Patients with T2D
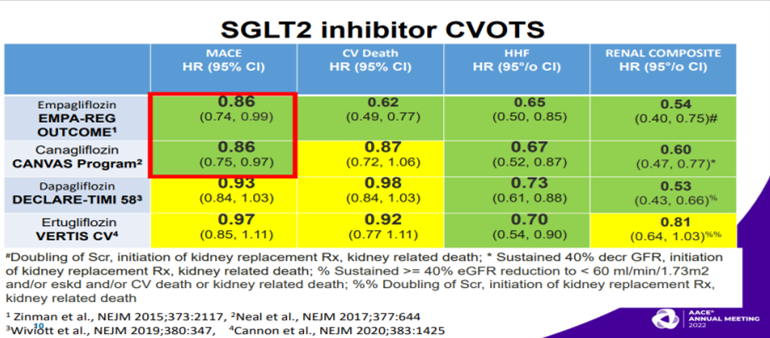
Blonde L, talked about pharmacotherapy of T2DM patients in a session at American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) Annual Meeting 2022 on 14th May, 2022. According to AACE 2020 and ADA 2022 guidelines, if patients have established or high risk for ASCVD, HF and/or CKD, then independent of glycemic control, targets and/or treatment [including metformin use] a GLP1-RA or SGLT2i with proven efficacy/benefit for the individual patient’s condition[s] is recommended as part of the glucose lowering regimen and comprehensive cardiovascular risk reduction. In SGLT2i CVOTs, EMPA-REG OUTCOME and CANVAS trials showed higher CV event rates as compared to DECLARE-TIMI 58, VERTIS CV. Also, SGLT2i showed non-significant results in non-fatal stroke in these 2 trials. GLP-1RA CVOTs showed that SUSTAIN-6 and REWIND trials had 39% and 24% RRR resp. in non-fatal stroke. In the IRIS (Insulin Resistance Intervention after Stroke Trial), Individuals with insulin resistance but no diabetes, recent history of ischemic stroke or TIA randomized to receive pioglitazone or placebo. Primary outcome of fatal or nonfatal stroke or MI occurred in 9% of those receiving pioglitazone vs. 11.8% of placebo group (p=0.007). Diabetes developed in 73 patients (3.8%) and 149 patients (7.7%) resp. (p<0.001). Pioglitazone associated with lower risk of stroke or MI and of diabetes but higher risks of weight gain, edema, and fracture. Low doses of pioglitazone <45 mg/d showed much of benefit with reduction in stroke , MI and new onset diabetes with less AEs other than fractures as compared to full dose. Empagliflozin, dapagliflozin have proven benefit canagliflozin has proven benefit [in those with diabetic nephropathy with albuminuria]. Empagliflozin and dapagliflozin HF benefits extend to those without T2D and for empagliflozin not limited to HFrEF. VERIFY trial showed that initial metformin and vildagliptin combination slowed decline of glycemic control as compared to metformin alone or vildagliptin added after to metformin. Several major trials i.e DAPA-HF, EMPUSE, EMPEROR-Reduced, EMPEROR-Preserved showed excellent reduction in CV events.
Clinicians could enter a patient’s characteristics and see from analysis of large numbers of similar patient, how they were treated and what their outcomes were. Pharmacogenetics is a study of genetic causes of individual variations in drug response. Pharmacogenomics has simultaneous impact of multiple mutations in the genome that may determine patient’s response to drug therapy. Ultimately merger of pharmacogenetics, pharmacogenomics, clinical data, and artificial intelligence using machine learning and derived algorithms may allow prediction of adverse outcome risks and treatments that can diminish them.
Successful Co-Management between Endocrinology and Primary Care – Diabetes
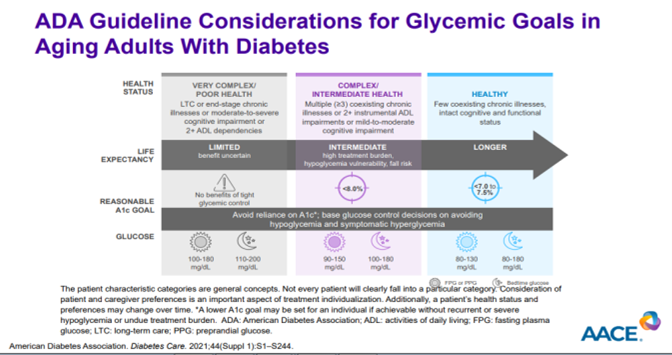
Wang CCL, presented a session on diabetes management at American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) Annual Meeting 2022 on 14th May, 2022. 4-Stage Progression Spectrum of Diabetes is 1) Insulin resistance 2) Prediabetes 3) T2DM 4) Vascular complications. T2D is a progressive disease in which intensification of management is needed over time. Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) may shorten life expectancy by 16 Years as compared to healthy individuals. Life span loss (16 years) with early DKD is much worse than with early CKD (6 years) or diabetes (10 years). Albuminuria can occur long before eGFR declines in DKD. Based on KDIGO 2011 guidelines, increase in urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) and eGFR is directly associated to increase in risk of all-cause mortality. As per Lancet study, ACR is an independent and better predictor of CV mortality than eGFR across the full range of kidney function. ACR ≥10 mg/g was significantly associated with increased CV mortality, but eGFR was not until. According to ADA 2022 and AACE 2020 guidelines, GLP-1 RAs can be used in place of metformin, if metformin is contraindicated or adverse events interfere or as part of initial combination therapy with metformin if A1C is 1.5%-2.0% above recommended levels or after metformin to avoid weight gain or hypoglycaemia. GLP1-RA and SGLT2i are preferred choice to minimize weight gain or promote weight loss. GLP1RA, SGLT2i, DPP-4i, TZD can be used to minimize hypoglycaemia. In people with T2D and ASCVD, GLP1-RA has proven CVD benefit and SGLT2 inhibitor can be used if eGFR is adequate. SGLT2 reduced HF and/or CKD progression if eGFR is adequate and GLP-1 RA is used if SGLT2i is contraindicated, not tolerated, or eGFR not adequate in T2D patients with HF and CKD. As per Lancet 2019, renal function decline was slowed with SGLT2 by 33% to 66% which showed improved renal outcomes in CVOTs. Major diabetes complications increase with age. Older patients had higher rates of eGFR and albuminuria. Severe hypoglycemia is associated with a higher risk of mortality. Also, hypoglycaemia increases the rate of thrombosis in T2D patients.
Diabetes treatment can now be individualized with we can now treat diabetes, not just chase blood sugar. Diabetes medications have glycemic benefit, but many also have cardiovascular and renal benefits. Hypoglycemia should be discussed at every visit: ask questions and review glucose data. New glucagon formulations make treatment easier, faster, and safer. Choose medications with lower hypoglycemia risks. A1C alone is insufficient for detecting hypoglycaemia. A1C is the OLD standard. CGM is the NEW standard.
Pharmacotherapy for Weight Management: Present and Future

Lofton H, presented a session on pharmacotherapy for weight management at American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) Annual Meeting on 14th May, 2022. NIH Consensus Statement on Pharmacotherapy for Weight Management includes:
- Adjunct to a comprehensive weight-loss programme that includes nutritional counselling and physical activity
- BMI of 30 kg/m2
- BMI of 27 kg/m2 with concomitant obesity-related risk factors or diseases
Newer agents introduced for weight management includes phentermine/topiramate, buproprion/Naltrexone XR, Liraglutide, Cellulose/Citric acid, and Semaglutide. The potential side-effects of phentermine/topiramate include paresthesia, dizziness, dysgeusia, insomnia, constipation, dry mouth and laboratory abnormalities may include metabolic acidosis, elevated creatinine, and lowering of glucose levels. The potential adverse events of buproprion/Naltrexone XR include nausea, constipation, headache, vomiting, dizziness, insomnia, and dry mouth.
Liraglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist and the potential side-effects of Liraglutide are nausea, diarrhoea, constipation, vomiting, headache, etc. Semaglutide causes a significant reduction in body weight as compared to placebo over a period of 68 weeks and was able to achieve ≥20% of weight loss in comparison to placebo.
To conclude, there are medications in pipeline such as Tirzepatide which has a GLP/GIP mechanism with patient experiences such as delayed gastric emptying, greater satiety, and increased energy expenditure. The administration is subcutaneous weekly and weight loss of 7-9.6Kg in T2DM. Another molecule is Cagrilintide which is a amylin analogue and has weekly subcutaneous administration.
Successful Co-Management between Endocrinology and Primary Care – Thyroid
Pearce E, presented a session on thyroid management at American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) Annual Meeting on 14th May, 2022. Common thyroid problems are Hypothyroidism, Hyperthyroidism (thyrotoxicosis), and Nodular thyroid disease. The ways to detect these thyroid problems are hormonal levels, testing of antibodies, and radiology and pathology.
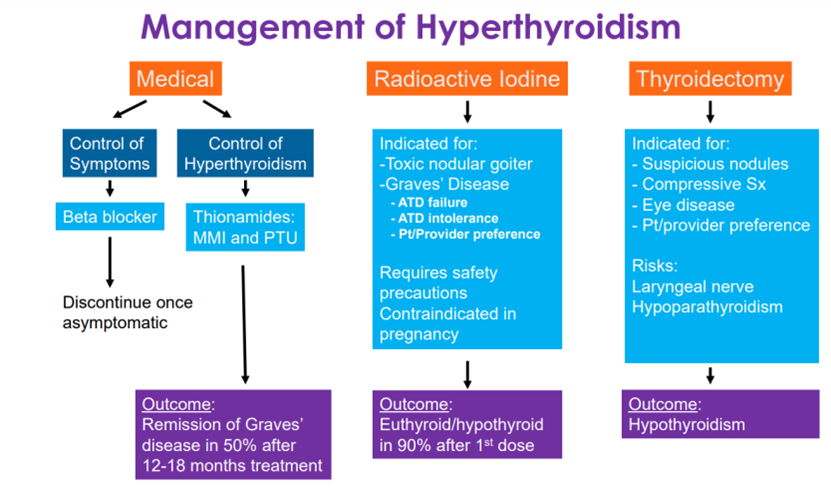
Causes of Hypothyroidism are autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto’s – most common), Previous thyroid surgery and/or therapy, iodine deficiency, and drug-induced. The treatment of choice in Hypothyroidism is levothyroxine (LT4). Use of LT3/LT4 combinations is not supported by evidence and T3-containing therapies should never be used during pregnancy. As soon as the pregnancy is announced, hypothyroid women should be advised to increase their LT4 dose by 25-30% which can be done by increasing their dose by 2 tablets weekly.
The medical management of hyperthyroidism includes MMI as a first-line agent (except in early pregnancy) and optimal treatment is for a period of 12-18 months. Thyroiditis is an Inflammatory destruction of thyroid follicular cells which has subacute and painless/post-partum phases. In the thyrotoxic phase of painless sporadic and postpartum thyroiditis, beta-blockers are recommended in the symptomatic treatment. In the symptomatic, hypothyroid Phase, treat with L-T4 for 6 months; then withdraw to determine whether thyroid function has normalized. Patients with thyroid nodules should be monitored closely and biopsy/re-biopsy need to be reconsidered if tumor grows > 50% in volume and > 20% increase in at least two nodule dimensions with minimal increase of 2 mm
In conclusion, there is no evidence to support LT3/LT4 combination therapy and Methimazole is preferred antithyroid medication over PTU and treatment is not required in all elderly patients with abnormal TSH.
Medical Management of Obesity Post-Bariatric Surgery Anti-Obesity Medications

Soleymani T, talked about obesity management after bariatric surgery in session at American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) Annual Meeting on 14th May, 2022. The main objectives are to identify Weight Regain & Insufficient Weight Loss in post-bariatric population, understand the role of anti-obesity drugs in the post-bariatric surgery, and identify the factors contributing to the selection of anti-obesity medications. Insufficient weight loss is defined as <50% excess weight loss at 18 months and there is no standard definition of weight regain.
The prevalence of weight regain post-LAGB, post-LSG, Post-RYGB are 38%, 27.8%, 3.9% respectively. The prevalence of insufficient weight loss post-LSG is 32-40% and post RYGB, AGB, and LSG combined is 20%. The underlying causes of WR and IW are hormonal, nutritional factors, physical inactivity, behavioural and anatomical factors, and genetics.
The prevention and management strategies include a multidisciplinary approach that consists of obesity Medicine Specialist, metabolic and bariatric surgeon, Dietitian, Behaviorist, Exercise trainer. The treatment options include bariatric surgery revision, endoscopic procedure, and anti-obesity medications. In a study of 319 patients with WR or IR, Topiramate demonstrated a statistically significant response for weight loss and were twice as likely to lose 10% of weight. In post-bariatric surgery weight management, when AOM was started at weight loss plateau, from pre-surgery to their new nadir weight, participants shed a higher percentage (41.2%) of their total body weight. When AOM initiated after weight regain, patients lost lesser percentage (−27.1%) of total body weight from pre-surgery to their new nadir weight
To conclude, weight regain after bariatric surgery is not uncommon and AOM are used for WR and IR. The best time to initiate AOM appears to be at postsurgical nadir weight OR when weight plateau is reached and post-operative bariatric patients treated with two or more anti-obesity medications have shown greater weight loss.
Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in the Inpatient Setting
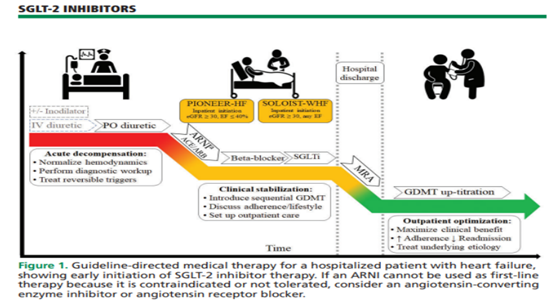
Gianchandani R, presented a session on SGLT2 inhibitors use in inpatient setting at American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) Annual Meeting on 14th May, 2022. Mr. T is a 60-year-old patient was diagnosed with non-ischemic heart failure with a decreased ejection fraction three months ago. Shortness of breath and exhaustion led to my first hospitalisation. T2DM for 5 years, successfully controlled with metformin and a healthy lifestyle (A1c- 6.8%). During admission, metformin was held. Prior to this hospitalisation, HF is titrating diuretics, ACEIs, and other cardiac medicines and cardiology team wants to start SGLT2 inhibitor while inpatient.
SGLT2 inhibitors works by reducing MACE events, heart failure and DKD. As per ADA algorithm of T2DM treatment based on co-morbidities, SGLT2i have proven benefits in the HF population.
As per DAPA-HF and EMPA-Reg, after SGLT2 Inhibitor initiation, effects were rapidly apparent within 4 weeks and sustained benefit was observed for 24 months. As per EMPA-Reg trial, Empagliflozin caused improvement in NYHA functional class at 28 days and sustained effect was observed for 52 weeks. As per SOLOIST Trial, Sotagliflozin was administered during or immediately after discharge (>50%). Hospitalizations and urgent visits for HF and CV fatalities have decreased. Patients with acute HF randomization within 3 days of hospitalization, had both new and chronic HF patients in trial, and had few patients with HFrEF and HFpEF. As per DARE-19 trial, 88% recovery was achieved with dapagliflozin as compared to 85% with placebo.
To conclude, starting SGLT2 inhibitors provides synergy with ongoing HF medications and maximises time of clinical benefit. It decreases hyperkalemia risk and time to benefit is reduced.
The Efficacy and Risks of SGLT2 Inhibitors
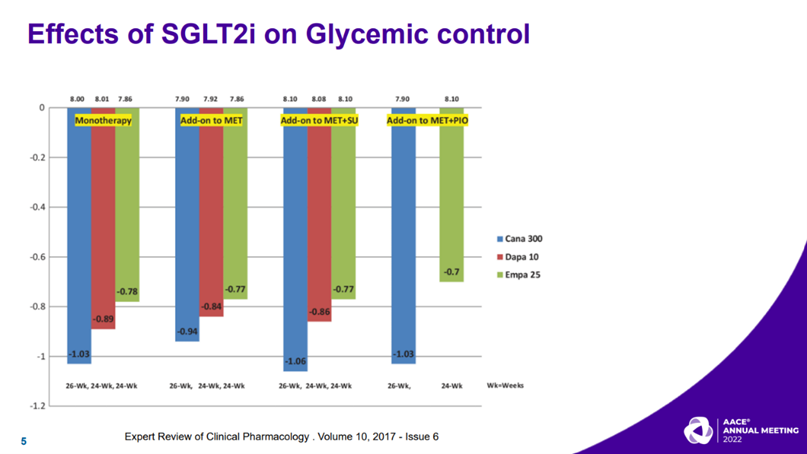
Rasouli N, presented a session on efficacy and risks of SGLT2is at American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) Annual Meeting on 14th May, 2022. The efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitors focuses on glucose lowering effects, cardioprotective effects, renal protection effects post MI and atrial fibrillation. Dapagliflozin and ertugliflozin were noninferior to empagliflozin and canagliflozin in reducing the composite outcome of MACE by 14%. People with T2D and established ASCVD benefit more from the cardioprotective benefits and the cardio-protective effects are not dose-dependent.
The heart failure quadruple therapy includes ARNI, beta-blockers, MRA, and SGLT2i. In individuals with T2D, all SGLT2 inhibitors reduce the incidence of HF hospitalisation and CV death. In people with HFrEF, dapagliflozin and empagliflozin lower the risk of HF hospitalisation and CV death regardless of T2D diagnosis. In persons with HFpEF, independent of T2D diagnosis, empagliflozin lowers the risk of HF hospitalisation and CV death.
One thing to keep in mind is that all SGLT2 inhibitors carry a ketoacidosis warning and the DKA occurred at an incidence of 0.6 to 2.2 occurrences per 1000 person-years in participants randomised to an SGLT2 inhibitor. The high-risk population includes ketogenic diets, history of alcohol abuse, history of severe gastroparesis and recurrent vomiting, patients who abruptly stop their insulin, hospitalized for major surgical procedures or acute serious medical illnesses. Ketone monitoring should be employed in high-risk population. Dapagliflozin and empagliflozin have not been associated with an increased risk of lower limb amputation
To conclude, SGLT2i have modest glucose-lowering effects and recommended as the first line therapy in T2D patients with HF. SGLT2i is part of quadruple therapy for HFrEF independent of the dx of DM.
Diabetic Muscle Infarction: An Uncommon Diabetic Complication with a Lack of Standardized Treatment
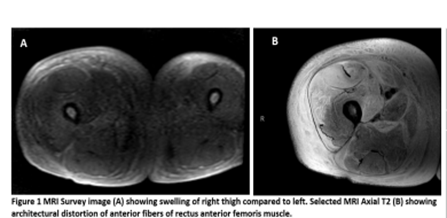
Suarez C, presented a session on diabetic muscle infarction at American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) Annual Meeting 2022 on 14th May, 2022. Diabetic muscle infarction (DMI) is a rare but deadly condition that has been linked to poorly managed diabetes. An African American man with end-stage renal failure presented with an unusual case of diabetic muscular infarction (ESRD) is presented. The difficulties in diagnosing and treating this uncommon illness are discussed.
A 42-year-old African-American man with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes and ESRD went to the hospital with acute new-onset right lower limb discomfort and swelling. The anterior medial thigh of the right lower leg was indurated, sensitive, and swollen, with pitting oedema and warmth to touch over the whole length of the thigh but sparing the inguinal and perineal regions, as well as the knee. The diagnosis of DMI was reached on clinical grounds, based on the patient’s history of poorly controlled diabetes, as well as the patient’s presentation and MRI findings. Low-dose aspirin, acetaminophen, and tighter glycemic control were given to the patient.
Following up with the patient, it was discovered that his thigh pain had improved, but the right thigh swelling had persisted for about 2-3 months. NSAIDs were avoided due to his ESRD with residual function. DMI is a rare diabetes complication that was first recorded in 1965. It’s most common in people who have advanced, poorly managed diabetes, with a mean HgA1C of 9.34% at the time of diagnosis. Although this ailment is usually self-limiting, NSAID treatment has demonstrated to have a faster healing time than bed rest alone, PT, or surgery. In individuals with renal illness, NSAID use may be restricted, thus pharmaceutical options should be investigated.
Diabetic myonecrosis, also known as muscular infarction, is a rare but serious illness that doctors must be aware of, given the rising frequency of diabetes mellitus. Due to its broad differential, it can present with a variety of clinical symptoms and can be difficult to identify. A clinical diagnosis can be made and validated with suggestive MRI results.

