ILLUMENATE: Four-Year Results with a Low-Dose Paclitaxel Drug-Coated Balloon in De Novo and Restenotic Femoropopliteal Lesions
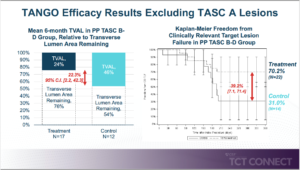
Holden A, presented findings of the ILLUMENATE trial at the TCT Connect 2020 virtual conference. All ILLUMENATE trials met their Primary Safety Endpoints with significantly lower major adverse event (MAE) rates (either individual or composite) vs. either PG or PTA control arms. In the short- to intermediate-term, paclitaxel coated balloons have shown protection and efficacy; however, long-term evidence, including all-cause mortality, remains small. The goal of this study is to continue evaluating the safety and efficiency of Stellarex Drug-Coated Balloon (DCB) in a large population of patients. For a low dose of paclitaxel DCB in de novo and restenotic femoropopliteal lesions from a large cohort, the delayed report on protection and efficacy performance was reported. The ILLUMENATE Global study is a prospective multi-center, single-arm study performed in the EU. The patient populations included those with a Rutherford Clinical Classification (RCC) of 2-4 and are recommended for de novo or restenotic lesions in the treatment of the superficial femoral artery (SFA) and/or popliteal artery. Office follow-up visits were post-procedure at 1, 6, 12, 24 and 36 months and included clinical, hemodynamic and functional outcomes. The primary safety endpoint was freedom from device- and procedure-related death through 30 days and freedom from target limb major amputation and CD-TLR through 12 months. The primary effectiveness endpoint was primary patency at 12 months. The primary safety endpoint was met by 77.9% (289/371) of the patients. The All-cause mortality rate was 8.1% in patients treated with stellarex. Freedom from primary safety event was 75.6% at 1460 days. The subgroup analysis showed there was no difference in prespecified cohorts from freedom from clinically-driven target lesion revascularization (CD-TLR) through 4 years.
Conclusion: The 4 year ILLUMENATE Global evidence indicates favorable safety and efficacy consistent with ILLUMENATE RCTs. The 4 yr ILLUMENATE Global data also shows similar efficacy in prespecified cohorts like gender and diabetics. The ILLUMENATE Global study confirms the Stellarex DCB’s stable long-term findings and is applicable to a complex population.
IN.PACT BTK: A Randomized Trial of Drug-Coated Balloon Angioplasty in the Infrapopliteal Arteries
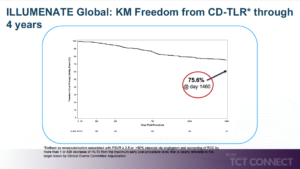
Micari A, presented findings of the IN.PACT BTK trial at the TCT Connect 2020 virtual conference. The aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of IN.PACT 014 BTK DCB versus percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) for treatment of patients with critical limb ischemia (CLI) and infrapopliteal chronic total occlusions (CTOs). The IN.PACT BTK Study was a prospective, multicenter, randomised pilot study involving CLI patients with Wlfi infrapopliteal lesions ≥ 40 mm, Rutherford level 4-5, infection grade 0-2, and ischemia grade 2-3. DCB (n=23; mean age 73.1 ± 7.4 years) or PTA (n=27; 69.6 ± 9.4 years) randomised to 1:1 participants. At 9 months post-procedure, the primary effectiveness endpoint was late lumen loss (LLL). The safety endpoint is a composite of freedom from device- and procedure related all-cause death within 30 days and freedom from major target limb amputation through 9 months and freedom from clinically driven target lesion revascularization (CD-TLR) through 9 months. A rigorous angiographic protocol for sub-segmental late lumen loss within the target lesion was performed to assess the totality of vessel narrowing. The mean lesion length for DCB and PTA was 215.4 ± 83.81 mm and 218.2 ± 80.43 mm respectively (p=0.806), and calcification was 54.1 % and 41.4 % respectively in the DCB and PTA classes (p=0.410). In the DCB group, LLL at 9 months was 0.89 ± 0.77 mm and in the PTA group, 1.31 ± 0.72 mm (p=0.070). In 91.3% of DCB and 87.5 % of PTA subjects (p=1.000), the safety composite endpoint was reached. At 9 months, all-cause mortality in both arms was low (4.3% DCB and 8.0% PTA; p=1.000) and there was no major target limb amputation in either arm. The additional sub-segmental angiographic measurements resulted in LLL of 0.592 ± 0.944 mm in the DCB group and 1.260 ± 0.810 mm in the PTA group (p=0.017).
Conclusion: The IN.PACT 014 BTK DCB demonstrates effectiveness through 9 months compared to PTA in a complex population. This novel, randomized, feasibility study with a .014 BTK balloon utilizing the 3.5 μg/mm2 IN.PACT drug formulation and enhanced study design provides opportunity to affect future BTK studies and treatment algorithms.
TANGO: A Randomized Dose-Escalation Trial of Temsirolimus Adventitial Delivery to Improve Below the Knee Outcomes
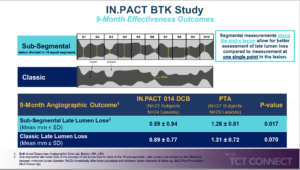
Armstrong E, presented findings of the TANGO trial at the TCT Connect 2020 virtual conference. This prospective, multicenter, dose-escalation, comparative, double-blinded study aimed to assess the 6-month efficacy and safety of the Bullfrog Micro-Infusion Device adventitial deposition of two escalating doses of temsirolimus in reducing angiographic neointimal hyperplasia and target lesion failure after revascularization of below-the-knee (BTK) arteries. 61 patients undergoing endovascular revascularization of ≥1 angiographically significant BTK lesions were enrolled. The primary and secondary efficacy endpoints were transverse-view vessel area loss percentage (TVAL%) of the target lesion and clinically relevant target lesion failure (CR-TLF) at 6 months respectively. The primary safety endpoint was freedom from a major adverse limb event or perioperative death (MALE+POD) at 30 days. The principal analysis was conducted in the per protocol (PP) community, which excluded subjects with unstented extreme dissections or unstented proximal total occlusions, as both of these may cause early failure unrelated to restenosis of the target lesion, and both will be excluded from potential enrollment in the study. Of 56 intent-to-treat (ITT) patients with 6-month follow-up, 8 were disqualified from the PP group. In the PP and PP-TASC B-D (excluding 15 subjects with TASC A lesions) subgroups, superior primary efficacy of the treatment arm was evident. In the PP and PP-TASC B-D subgroups at 6 months, respectively, TVAL reductions of 13.9 % and 22.3 % were observed. In those patients treated with temsirolimus, the freedom from CR-TLF rates was significantly higher. In the PP and PP-TASC B-D subgroups, the disparities between treatment and control for 6-month CRTLF independence were 27.1 % and 39.2 %, respectively. Freedom from composite of 30-day MALE+POD was 100% in all groups.
Conclusion: In the TANGO study, excellent safety results were shown, and the primary and secondary efficacy measures indicators were encouraging. Findings indicate that adventitial temsirolimus deposition using the Bullfrog Micro-Infusion System increases vessel patentability for 6 months after effective endovascular revascularization when applied to BTK arteries.
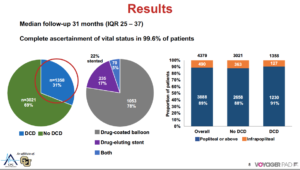
VOYAGER PAD: Long-Term Safety of Drug-Coated Devices In Peripheral Artery Revascularization
Hess CN, presented findings of the VOYAGER PAD trial at the TCT Connect 2020 virtual conference. VOYAGER PAD was a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of PAD patients undergoing lower extremity revascularization (LER) randomized to rivaroxaban 2.5 mg twice daily or placebo on a background of aspirin 100 mg daily. Clopidogrel was allowed per operator discretion. The primary findings of this study showed that rivaroxaban was associated with a substantially lower incidence of acute limb ischemia, major amputation for vascular causes, myocardial infarction, ischaemic stroke, or death from cardiovascular causes at a dosage of 2.5 mg twice daily plus aspirin than with aspirin alone. The long-term safety of DCD was explored in this study and assessed whether rivaroxaban 2.5 mg twice daily plus low dose aspirin versus low dose aspirin alone on the primary efficacy endpoint was consistent with versus without DCD use. Of the 6,564 randomised patients, 66% (n=4,316) underwent and were included in the endovascular index LER in this analysis; the median follow-up was 31 months (IQR 25, 37) and 99.6% of the patients had full ascertainment of vital status. DCD was used by 31 % (n=1,358) of patients during the qualifying endovascular LER. More often, patients receiving DCD had previous endovascular LER, had higher baseline usage of dual antiplatelet and statin therapy, and were treated more often for claudication than non-DCD patients. Lower associated mortality among patients receiving DCD and non-DCD was observed in the unweighted analysis (2.9 vs. 3.9 per 100 patient-years; 3.5-year Kaplan-Meier cumulative incidence of 10.2 % vs.13.8 %). There was no correlation between DCD use and mortality after weighting (3.5-year cumulative incidence 12.1% vs. 12.6%, HR 0.95, 95 % CI 0.83-1.09, p=0.49) after weighting. The value of rivaroxaban 2.5 mg twice daily with aspirin is ischemic limb reduction and cardiovascular outcomes relative to aspirin alone. Compared to aspirin alone, the benefit of rivaroxaban 2.5 mg twice daily with aspirin in reducing ischaemic limb and cardiovascular outcomes was also consistent, irrespective of whether DCD was used.
Conclusion: The value of twice daily rivaroxaban 2.5 mg with aspirin versus aspirin alone in reducing ischaemic limb and cardiovascular outcomes for symptomatic PAD after revascularization is consistent independent of DCD usage.
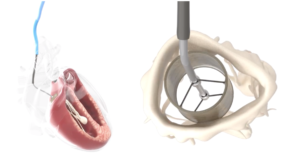
Percutaneous Tricuspid Valve Repair Using the CroiValve Duo Device
Quinn M, presented a study which assessed the use of CroiValve Duo Device at the TCT Connect 2020 virtual conference. Tricuspid regurgitation (TR) is prevalent and can contribute to substantial morbidity and mortality. The authors created the CroiValve Duo, a new easy-to-use percutaneous tricuspid valve repair system that supports leaflet coaptation. The device is intended for the care of all patients, including those with severe right heart dilation. In a bench-based tricuspid regurgitation (TR) model, the efficacy of the CroiValve Duo system was tested ex vivo using an excised porcine tricuspid valve sewn into an oversized ring dilated to over 5 cm in a pulsatile system to reproduce annular dilation. In vivo studies were performed in ovine and porcine animal models. High-dose intravenous beta blockade or pulmonary artery banding and pulmonary valve ligation induced tricuspid regurgitation. Under x-ray and echo guidance, the device was administered via the internal jugular. The efficacy of the device was tested by intracardiac echo after 30 and 90 days. In both bench-based and animal models, the CroiValve Duo device reduces tricuspid regurgitation from severe to moderate. The device is easy to deliver and secure. The device stayed in a comfortable place and did not induce trauma to the native leaflets or right heart with longer-term follow-up, 30 and 90 days.
Conclusion: The CroiValve Duo device is safe and easy to use. It is designed to treat all-comers including those with significantly dilated right hearts. It significantly reduces tricuspid regurgitation in bench based and animal models of TR.
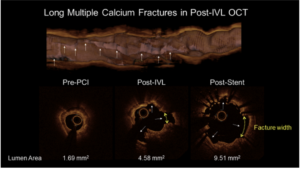
Intravascular Lithotripsy for Treatment of Severely Calcified Coronary Stenoses: Results from the Disrupt CAD III Optical Coherence Tomography Sub-study
Shlofmitz R, presented findings from the substudy of Disrupt CAD III OCT at the TCT Connect 2020 virtual conference. Disrupt CAD III OCT substudy sought to confirm the mechanism of calcium modification after IVL treatment and the impact of IVL on implantation of the coronary stent. The OCT substudy included 100 patients enrolled in the Disrupt CAD III study of severely calcified lesions. The pre-IVL, post-IVL, and post-stent OCT images were analysed by an independent OCT core laboratory (Cardiovascular Research Foundation, New York, New York). Pre-procedure OCT results (mean ± SD) showed a minimum lumen area of 2.2 ± 0.8 mm2, 72 percent ± 12 % area stenosis, 31.6 ± 10.2 mm lesion length, and 292 ° ± 77 ° gross superficial calcium angle. In 67 % of the lesions, circumferential and longitudinal calcium fractures were found post-IVL. The acute area gain in post-IVL was 1.4 ± 1.1 mm2. The minimum stent area after stent implantation was 6.5 ± 2.0 mm2, driven by an increase in the width of the fracture from 0.55 ± 0.45 mm post-IVL to 1.32 ± 1.04 mm post-stent (p < 0.0001). Stent expansion at the original site of maximum calcium was 102% ± 29%.
Conclusion: OCT imaging after coronary IVL in severely calcified vessels demonstrated calcium fractures in two-thirds of lesions, which facilitated an increase in minimum stent area and excellent stent expansion.
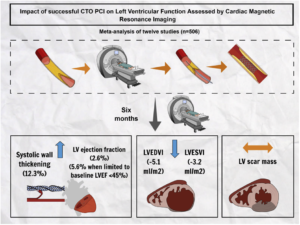
Impact of Chronic Total Occlusion Revascularization on Left Ventricular Function Assessed by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance
The effect of chronic total occlusion (CTO) percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) on left ventricular (LV) function, remodeling, and systolic wall thickening (SWT) measured by cardiac magnetic resonance is contentious. Megaly M, presented a study at TCT Connect 2020 virtual conference which executed a meta-analysis of all published studies outlining cardiac magnetic resonance parameters of LV function prior and following successful CTO PCI. 12 studies (1 randomized controlled trial and 11 observational studies) (n = 506 patients) were included. Approximately 40% of patients showed a prior myocardial infarction, and 12.4% showed prior bypass surgery. The median follow-up time for the study was 6 months (interquartile range: 4.25 to 6). Following successful CTO PCI, which was not dependent on the presence of myocardial feasibility in all studies, a substantial increase was seen in regional SWT in dysfunctional segments provided by the CTO vessel (MD 12.3%; 95% [CI]: 6.6 to 17.9%; p < 0.001), reduction in LV end-diastolic volume index (MD -5.1 ml/m2; 95% CI: -7.7 to -2.6 ml/m2; p < 0.001) and LV end-systolic volume index (MD -3.2 ml/m2; 95% CI: -5.3 to -1.0 ml/m2; p < 0.001), and enhancement in LV ejection fraction (LVEF) (MD 2.6 %; 95% CI: 1.5 to 3.7%; p < 0.001; I2 = 0%), which were further pronounced when the evaluation was restricted to studies with baseline LVEF below 45% (MD 5.5%; 95% CI: 2.8 to 8.2%; p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Successful CTO PCI showed substantial enhancement in regional SWT in dysfunctional segments provided by the CTO vessel with enhancement in LVEF, particularly when baseline LVEF is decreased. Myocardial viability requires to be combined into future CTO studies.
The Impact of Myocardial Fibrosis on Alcohol Septal Ablation Success
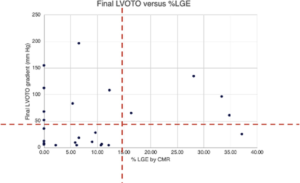
Alcohol septal ablation (ASA) is specified to reduce medically refractory left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction between hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients. Earlier studies recommend that up to 20% of cases may be unsuccessful, so recognising predictors of success is clinically relevant. Makani A, presented a study at TCT Connect 2020 virtual conference which assessed the correlation among the range of myocardial fibrosis by means of late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) and LVOT gradient decrease. Consecutive ASA cases were retrospectively reviewed during 2016 and 2020 at the institution. Baseline estimations including septal thickness and LVOT gradient, cardiac magnetic resonance late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) and quantitative estimation, and intraprocedural gradients were acquired. The LVOT gradient was analysed using an echocardiogram and procedural success was described as a LVOT gradient <50 mm Hg at 6 months. At the 1-year follow-up, 33 patients underwent ASA, with no complications of mortality or ventricular septal defect. 11 of the 33 showed peak LVOT gradient <50 mm Hg at the 1-year follow-up. Patients with LGE <15% showed a 75% chance of procedural success as compared to a 20% success rate for those with greater LGE extent (p = 0.033) (Figure).
Conclusion: This was the first report of the correlation among septal fibrosis (as estimated by cardiac magnetic resonance LGE) and LVOT gradient decrease in patients experiencing ASA. Greater baseline fibrosis extent seems to be correlated with lower chances of success. This examination may reflect the procedure by which alcohol generates myocardial thinning via necrosis of feasible myocytes.
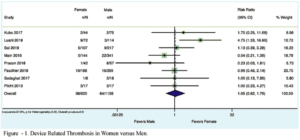
Meta-Analysis of Device-Related Thrombosis After Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion in Women Versus Men
Women show an enhanced occurrence of device-related thrombosis (DRT) following percutaneous left atrial appendage occlusion (PLAAO), which is correlated with a greater risk of stroke. Nevertheless, women were under-represented in the landmark trials causing the Food and Drug Administration approval of PLAAO. There is a lack of comparative studies which explored the effect of sex on DRT following PLAAO. Ghaffar YA, presented a study at TCT Connect 2020 virtual conference which assessed sex disparity in DRT following LAAO. The authors executed a literature search in PubMed, Google Scholar, and ClinicalTrials.gov and incorporated studies outlining DRT. A data was gathered on the clinical outcomes and measured relative risk (RR) and 95% CI for DRT in males versus females. A random effect was used to combine the consequences. In the evaluation, 8 clinical studies with a total of 1,764 patients were incorporated. The overall population comprised of 35% females, with a mean age of 75 ± 8.4 years. In the overall group, 78% patients showed hypertension, 24% patients showed prior stroke, 27% patients showed diabetes mellitus, and 23% patients showed congestive heart failure. No difference was seen in DRT in women versus men (RR:1.05; 95% CI: 0.62 to 1.79: p = 0.8; I2 = 27.6%).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis did not discover a substantial difference of DRT post-implantation among males versus females. It should, nevertheless, be acknowledged that DRT is outlined as a binary occurrence with no details on thrombus size and load. There are variabilities in imaging protocols applied to characterize DRT, and single-center registry data may be restricted with reporting bias.
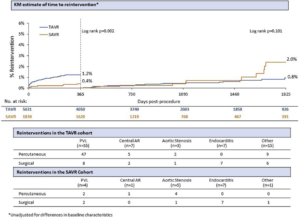
Reinterventions After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement with a Supra-Annular Self-Expanding Bioprosthesis
In patients with serious, symptomatic aortic stenosis, transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is an option. Longer-term protection and longevity, particularly in younger, low-risk patients, affect patient selection. Grubb K, presented a study at TCT Connect 2020 virtual conference which analysed 5- year reintervention occurrences following self-expanding TAVR and surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR). Data were gathered from 5 trials (CoreValve US Pivotal Extreme-Risk and High-Risk Trial and Continued Access Studies, SURTAVI and SURTAVI Continued Access Study, and Evolut Low Risk) incorporating 5,631 TAVR and 1,839 SAVR patients. All patients experienced annual echocardiography, and mediated at the physician’s discretion. An early and late reinterventions were compared using Kaplan-Meier analysis and details were classified by symptom and therapy. 87 TAVRs and 18 SAVRs showed reintervention; 1-year Kaplan-Meier reintervention rates were substantially greater for TAVR versus SAVR however comparable among 1 and 5 years, while SAVR patients more reinterventions after 1 year. The most frequent cause for reintervention was paravalvular leak following TAVR and endocarditis after SAVR. Valve-in-valve reinterventions was predominated, besides in endocarditis.
Conclusion: This post hoc evaluation of pooled data from more than 7,000 patients showed low rates of reintervention following TAVR and SAVR via 5 years, with early reinterventions arising more commonly with TAVR and late reinterventions following SAVR. Further analyses of reinterventions per indication and timing as well as effects of reintervention will be yielded at the time of the meeting.
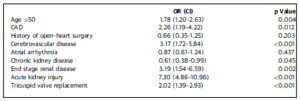
Predictors of Mortality After Isolated Tricuspid Valve Surgery
Isolated tricuspid valve surgeries (TVSs) are not frequently executed and are correlated with a greater operative mortality rate of 5% to 44%. Peerbhai S, presented a study at TCT Connect 2020 virtual conference which recognised risk factors correlated with mortality following isolated TVS in the United States. The patients who experienced isolated target vessel revascularization were recognised from the 2005 to 2014 National Inpatient Sample database. Patients with congenital heart disease or endocarditis and those undergoing concomitant cardiac operations were eliminated. A logistic regression model was assembled to recognise the predictors of mortality following isolated TVS. From the 9,784 patients experienced isolated TVR, 748 (7.6%) patients died during the index hospitalization. On multivariate regression evaluation, substantial predictors of mortality recognised included age >50 years (odds ratio [OR]: 1.78; 95% CI: 1.20 to 2.63), presence of coronary artery disease (OR: 2.25; 95% CI: 1.19 to 4.22), cerebrovascular disease (OR: 3.16; 95% CI: 1.71 to 5.84), acute kidney injury (OR: 7.30; 95% CI: 4.86 to 10.96), end-stage renal disease (OR: 3.19; 95% CI: 1.54 to 6.59), and tricuspid valve replacement (OR: 2.02; 95% CI: 1.39 to 2.93).
Conclusion: The mortality correlated with isolated TVS has not changed across the study period. Patients undergoing tricuspid replacement showed higher mortality than repair. Other factors correlated with mortality incorporate age >50 years, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, acute kidney injury, and end-stage renal disease.
ICE-Guided LAA Closure with a Conformable Foam Implant
Left atrial appendage closure (LAAC) in patients who are weak candidates for long-term oral anticoagulants has been a primary atrial fibrillation stroke prevention technique. Limitations of existing LAAC systems include the requirement for accurate coaxial delivery, painful implantation potential, inadequate left atrial appendage (LAA) sealing, and device-related thrombus dissipation that prompts transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) instruction to be performed on most LAAC procedures. Reddy V, presented a study at TCT Connect 2020 virtual conference which assessed intracardiac echocardiography (ICE)-guided implantation of the Conformal Left Atrial Appendage Seal (CLAAS) implant (Conformal Medical, Inc., Nashua, New Hampshire). The CLAAS implant showed a nitinol endoskeleton with a porous foam cup accessible in 2 sizes (regular and large). It was brought under fluoroscopic and ICE guidance and under conscious sedation in a prospective single-center series. Following positioning, TEE was placed to affirm ICE findings preceding to device release. A dual antiplatelet treatment was given for 6 months following closure. 15 patients gone through LAAC (age 71.3 ± 10.8 years, 33% male, CHA2DS2-VASc 4.1 ± 1.7, LAA diameter 11 to 28 mm). Implantation was 100% successful, taking 55.1 ± 20.6 minutes with 41.5 ± 14.5 ml contrast. TEE analysis preceding to final release showed sufficient seal in all patients. There were no procedure/device-associated complications. In 11 of 11 patients (4 missed TEE because of COVID-19), TEE showed a sufficient seal at 45 days (9 patients, no leak; 1 patient, 1 mm; 1 patient, 2 mm) and no device-associated thrombus.
Conclusion: ICE-guided LAAC with the CLAAS implant is viable and LAA seal showed good consequences in conscious sedation.