Attitude and Perception of People with Type 2 DM about Obesity- A Western Indian Perspective
Patange S. presented a study in a session at 83rd Scientific Sessions of American Diabetes Association. Obesity plays a significant role in the increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Among obese individuals in India, the lifetime risk of developing T2DM is remarkably high, estimated at 86.0% [76.6, 91.5] %. This study aims to assess the attitudes and perceptions of the general Indian public with T2DM towards obesity and its management.
A cross-sectional survey was conducted between October and November 2022 at 30 diabetes care clinics in Western India. A structured questionnaire was administered to consenting male and female participants aged ≥18 years. Descriptive statistics were used to analyze the collected survey data.
A total of 1248 subjects (592 males and 658 females) with a mean (SD) age of 44.6 (14.8) years participated in the survey. Among them, 596 (47.8%) had T2DM, with a mean (SD) BMI of 29.9 (5.7) kg/m². Of the 596 T2DM subjects, 203 (34.1%) perceived their weight as normal, 305 (51.2%) considered themselves overweight, and 88 (14.8%) identified as individuals with obesity. However, when classified based on the Asia-Pacific guidelines for obesity classification of BMI, it was found that 544 (91.4%) T2DM subjects were either overweight or obese. Among these 544 subjects, the top two weight management programs they were aware of where diet consultations for weight loss (374; 68.8%) and gym memberships (269; 49.4%). Furthermore, 396 (72.8%) believed that eating less and moving more is a simple formula for weight loss. Although 303 (55.7%) subjects were aware of doctors- prescribed weight loss drugs, only 291 (53.5%) were considering weight management, and only 228 (41.9%) were willing to try these medications. The top two co-morbid conditions in overweight or obese T2DM subjects were high blood pressure (41.2%) and knee pain/mobility issues (12.9%).
This survey highlights a lack of awareness regarding the impact of obesity among Indian T2DM subjects who are overweight or obese. Educating individuals about the benefits of weight management interventions can contribute to optimizing outcomes for T2DM patients.
Two-Year Results from a Novel, Patient-Centered, Team-Based Intervention for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes at High Cardiovascular Risk
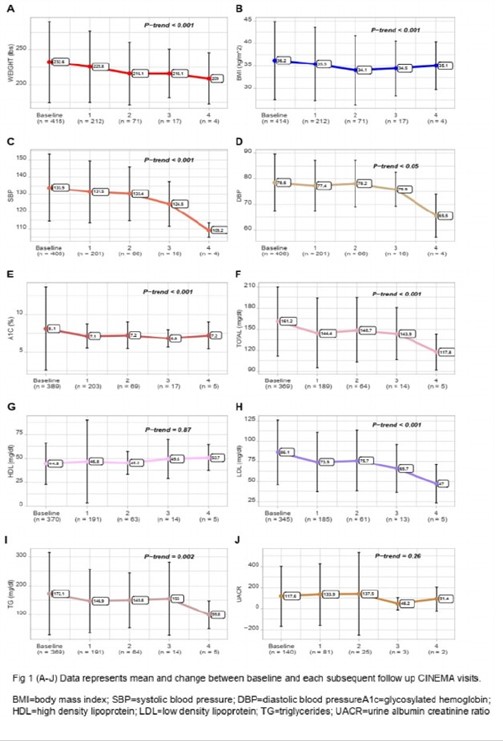
Arafah A, presented a study at the 83rd Scientific Sessions American Diabetes Association on June 26, 2023. Therapy patterns were analyzed in the LANDMARC study, a prospective observational study (CTRI/2017/05/008452), involving participants with type 2 diabetes (T2D) using two or more antihyperglycemic medications. Out of the 6222 evaluable participants (mean baseline values – age: 52.1 yrs, T2D duration: 8.6 yrs, A1C: 8.05%), 5273 completed the 3-year follow-up. Treatment decisions were made by the treating physicians.
After three years, the percentage of participants using insulin in combination with oral antidiabetic drugs (OAD) increased from 23.95% to 34.86%, while the percentage of those using only OADs decreased from 74.51% to 63.30%. Among injectable glucose-lowering drugs, there was an increase in the use of basal, prandial, and premix insulin. The most commonly used OAD classes were biguanides and sulfonylureas. There was a significant increase in the addition of DPP4 inhibitors (from 48.91% to 62.44%) and SGLT2 inhibitors (from 10.51% to 23.39%).
Overall, the insulin subgroup showed improvements in glycemic parameters compared to the insulin-naïve subgroup (p<0.0001). There was no significant difference in glycemic parameter changes between those on basal insulin and those on premix insulin. These findings suggest that timely intensification of therapy may play a crucial role in improving glycemic control.
Are Two Better than One? Initial Combination Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Pro
DeFronzo R, at the 83rd Scientific Session of the ADA 2023 presented a session on “Are Two Better than One? Initial Combination Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Pro”
DeFronzo addressed that the reson for failure to achieve glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients are mainly the complex pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes, “Treat to Fail” approach of monotherapy and physician inertia results in delay in initiating therapy. Treatment of T2DM:
- Will require multiple drugs in combination to correct multiple pathophysiologic defects
- Should be based upon known pathogenic abnormalities, and NOT simply on the reduction in HbA1c
- Must be started early in the natural history of T2DM, if progressive beta cell failure is to be
The ideal algorithm for initiating drugs in T2DM is the DeFronzo Algorithm as below. This algorithm utilizes the cardio- renal-metabolic drugs in combination.
- GLP-1 RA: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists
- SGLT2i: Sodium/glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors
- Pioglitazone
- Metformin
The top three medicines do have cardiovascular and renal advantages. When looking at the ominous octet, GLP-1 RA deserves six stars because it is an excellent monotherapy medicine. Metformin and sulphonylurea are two medicines that plainly do not work long term. GLP-1 RA, SGLT2i, and pioglitazone are the only medicines that function. In this new era of therapy, it is necessary not only to reduce HbA1c but also to stimulate weight reduction, which will indirectly increase insulin sensitivity.
The EDICT research clearly demonstrates the advantages of combined treatment. The findings of this exploratory investigation demonstrate that combination treatment with metformin/pioglitazone/exenatide is more effective and resulting in better outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed T2DM than sequential add-on therapy with metformin, sulfonylurea, and then basal insulin.
As T2D is a progressive condition, maintaining glycemic goals with monotherapy is sometimes only doable for a few years. Traditional advice has been to add medicines to metformin in a stepwise manner. However, there is evidence to recommend early combination treatment for more quick achievement of glycemic targets and longer glycemic impact durability.
SGLT2 Inhibitors Are Associated with Kidney Benefits at All Degrees of Proteinuria—A Cohort Study
Fujita at the 83rd Scientific Session of the ADA 2023 presented the findings of a retrospective cohort study to examine the effectiveness of SGLT2i compared to dipeptidyl dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP4i), in Alberta, Canada.
A cohort was created of SGLT2i new users (2014-2018) with diabetes and eGFR ≥30 mL/min/1.73 m2 albuminuria using administrative data. New SGLT2i users were matched 1:1 to DPP4i users based on CKD stage, albuminuria, and diabetes treatment, as well as time-conditional propensity-score (age, gender, A1c, and so on). A urine albumin to creatinine ratio of ≤ 30 mg/mmol was defined as non- severe albuminuria. Linear and Poisson regression models were used to determine adverse determine the association of SGLT2i use with each outcome: eGFR decline (acute [≤ 60 days] and total), adverse kidney events, and all-cause mortality. Adverse kidney event was defined as sustained 40% loss of eGFR, initiation of kidney replacement therapy, or death from kidney causes.
SGLT2i users (n=19,238) had a mean age of 57.9 years (male 59.1%) and non-severe albuminuria in 94.4%. Mean eGFR was 91.7 mL/min/1.73m2, and 62.0% were dispensed ACE inhibitor or ARB. Median follow- up was 1.58 years (IQR 0.91-2.49). The acute change in eGFR was -2.79 (SGLT2i) vs -1.43 (DPP41), for a difference of -1.36 (95% CI -1.74- [-0.98], p < 0.001). After day 60, SGLT2i use was associated with 0.83 (0.66- 1.01, p < 0.001) less annual eGFR loss than in DPP4i users. SGLT2i use was associated with fewer adverse kidney events (IRR 0.58 [0.47-0.71], p < 0.001), driven mostly by less sustained loss of eGFR, but was not associated with all-cause mortality (IR 0.82 [0.66-1.01], p= 0.06). Similar findings were observed in those with non-severe albuminuria.
SGLT2i, independent of baseline albuminuria status, may prevent eGFR deterioration and minimize the incidence of serious renal events in persons with diabetes.
Higher Hydration Status Is Indicative of Tolerance of Better Glucose Tolerance
Water intake is an important dietary behavior to replace high-caloric beverages and to enhance metabolic health. Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder that has been shown to be more prevalent in Hispanics, a population shown to consume relatively less water compared to non-Hispanic Whites. The underlying cause of type 2 diabetes is insulin resistance, characterized by hyperglycemia and impaired glycemic control.
Apaflo J, presented a study at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) held in San Deigo, United States between 23rd-26th June 2023 that evaluated whether hydration status indicates glucose tolerance among a dominant Mexican American population. The study included sixty-one participants without diabetes (Age: 26.5 ± 9.1 years; BMI: 27.5± 6.0 kg/m2) Fasting blood glucose level was determined, and a 2-hour glucose tolerance test was performed following the ingestion of a 75g glucose drink. Blood glucose concentration levels were determined at 15-, 30-,60-, 90-, and 120-minute time intervals post ingestion, and the glucose area under the curve was analyzed as well. Blood works were performed to determine blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine concentrations. Hydration status was estimated using the ratio of BUN to creatinine values. Hydration status measured by BUN/Creatinine was positively associated with glucose intolerance measured at 15-, 30-, 60-, and 90-minute post glucose load and by glucose area under the curve (r=0.33; r=0.43; r=0.37; r=0.27; and r=0.41 respectively; p<0.05).
Adequate fluid consumption should be encouraged for glycemic control, especially among people with high diabetes risks.
Complications of Diabetes after 15 Years—Comparing Telemedicine with Conventional Care
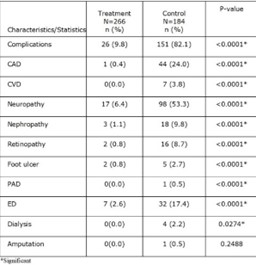
Table 1: Micro-macro vascular complications
Diabetes Tele-Management System (DTMS®), a telemedicine (TM)-based intervention and follow-up program for diabetes management comprising of a multidisciplinary team performs drug titration, provides dietary advice & educates the patients and their caregivers periodically with the help of customized software and user interface.
Kesavadev J, presented study results at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) held in San Deigo, United States between 23rd-26th June 2023 that evaluated the long-term effect of TM consultation along with face-to-face consultation (F-F) in metabolic control & prevention of complications.
A total of 495 T2D (62.91 ± 11.64 years (Y); 62.2% males, duration of diabetes: 8.41 ± 2.78 Y), were de-identified. The treatment group [TG- 63.41±11.73 Y; 62.92% males; 8.04± matched 8.04±1.82 Y of T2D] included T2D with ≥1F-F and ≥5 TM consultations per year. The propensity score-matched control regular control group [CG-62.17±11.50 Y; 58.69% males; 7.98±2.96 Y of T2D] included T2D who were not on regular follow-statistically follow-up with compromised F-F and TM visits. Data of 15±5 years were collected from DTMS and statistically analyzed.
Significant improvement (p < 0.001) in clinical parameters including HbA1c, FBS, lipid profile, BP & weight diabetic weight from baseline to 10 Y of follow up was observed in TG. 9.8% of TG and 82.1% of CG had diabetic complications and arms complications (Table 1).
This 15-year-long real-world experience reveals a robust difference between the 2 arms providing compelling evidence to fund TM consultations.
Integrated Approach of Yoga Therapy((IAYT) Improves Cerebrovascular Functions and Prefrontal Hemodynamic Activities Related to Cognition in Type 2 Diabetes
Singh D assessed the integrated approach of yoga therapy (IAYT) effect on cerebrovascular reactivity in middle cerebral artery (MCA), prefrontal cortex (PFC) oxygenation, and cognitive functions in patients with T2DM and discussed the results at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) held in San Deigo, United States between 23rd-26th June 2023.
In this study, 75 patients were randomized to the IAYT group [n=38; 07 female; mean age 52.95(8.20) years] and the waitlist control group [n=37; 06 female; mean age (SD) 49.62(10.94) years]. The cerebral blood flow and prefrontal hemodynamic activities were assessed using transcranial doppler and functional near-infrared spectroscopy, respectively, during resting and cognitive performance. IAYT group participants received 3 months of intervention and assessments were done at baseline (0-week), mid (after 6-week), and post (after 12- week).
After a 12-week intervention, participants of the yoga group showed improved accuracy and reaction time in a 2-back condition of the working memory task, and the scores of the Corsi Block Tapping task. Further, cerebrovascular changes were observed in the middle cerebral artery, which showed increased peak systolic velocity, mean blood flow velocity, end-diastolic velocity, and breath-holding index after 12-week yoga practice. The oxygenation was also higher at dorsolateral, dorsomedial, and ventromedial and orbitofrontal PFC in the 12th week of the yoga practitioners group compared to the control group. Moreover, during 2-back working memory task, yoga group participants demonstrated increased oxygenation at dorsolateral PFC compared to preland higher oxygenation at dorsolateral, ventrolateral, ventromedial and orbitofrontal PFC compared to control group.
The results suggest that IAYT practice may improve cognitive functions by improving cerebral blood flow through the middle cerebral artery and hemodynamic activities in the prefrontal regions in patients with T2DM.

