Bocchi EA. ESC Heart Failure. 2018; 5: 249–256.
The SHIFT trial demonstrated that Ivabradine decreased heart rate (HR) and the hazard of cardiovascular outcomes. For the efficacy and safety of Ivabradine, concerns persist on heart failure (HF) caused due to Chagas disease (ChD). Bocchi EA, et al., conducted a post hoc analysis of the SHIFT trial to examine the effect of Ivabradine in patients with ChD HF.
SHIFT trial was conducted in patients with symptomatic systolic stable HF, HR ≥ 70 b.p.m., and in sinus rhythm. The ChD HF subgroup randomised 38 patients to Ivabradine (n=20), and placebo (n=18). A higher prevalence of bundle branch right block, lower systolic blood pressure; increased use of diuretics, cardiac glycosides, and anti-aldosterone agents; and decreased use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/angiotensin II receptor blocker or target daily dose of beta-blocker was noticed in the ChD HF subgroup as compared with the overall SHIFT population.
ChD HF conferred a poor prognosis (all-cause mortality at 2 years was ~60%. The mean twice-daily dose of Ivabradine was 6.26 ± 1.15 mg and placebo 6.43 ± 1.55 mg. Ivabradine shows significant reduction in HR from 77.9 ± 3.8 to 62.3 ± 10.1 b.p.m. (p = 0.005) [Figure 1].
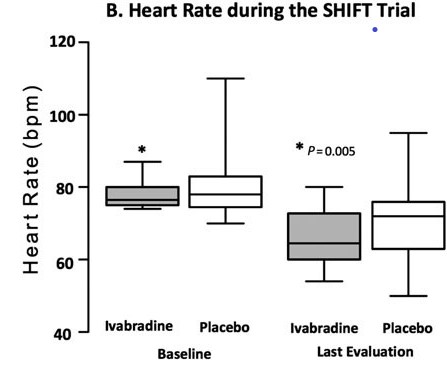
Figure 1. Heart rate during the follow-up in patients with Chagas disease heart failure treated with ivabradine and placebo (with intragroup paired t-test P value).
Ivabradine shows improvement in functional class in 30% of patients, whereas functional class remained stable in 60% of patients and worsened in 10% of patients. The functional class improved in 22% of patients, remained stable in 44%, and worsened in 33% with placebo [Figure 2].
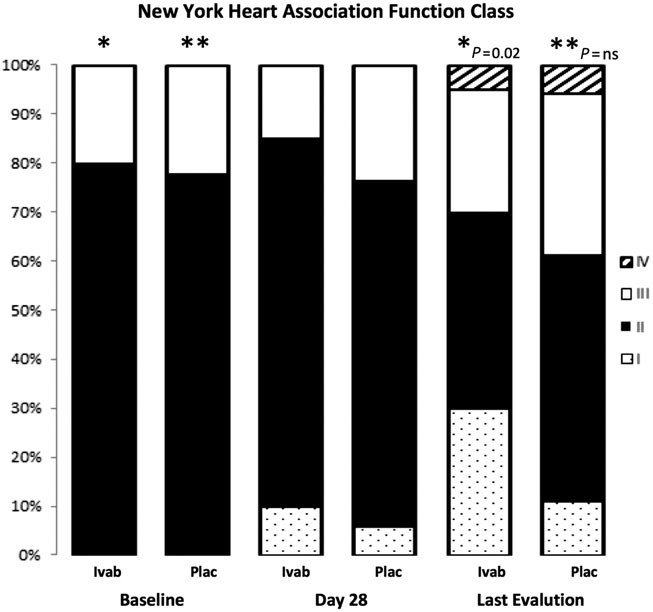
Figure 2. New York Heart Association functional class at baseline and during the follow-up in patients with Chagas disease heart failure treated with Ivabradine and placebo
Ivabradine shows reduction in all-cause death as compared to placebo (p = 0.07) [Figure 3]. Ivabradine was not correlated with serious bradycardia, atrioventricular block, hypotension, or syncope.
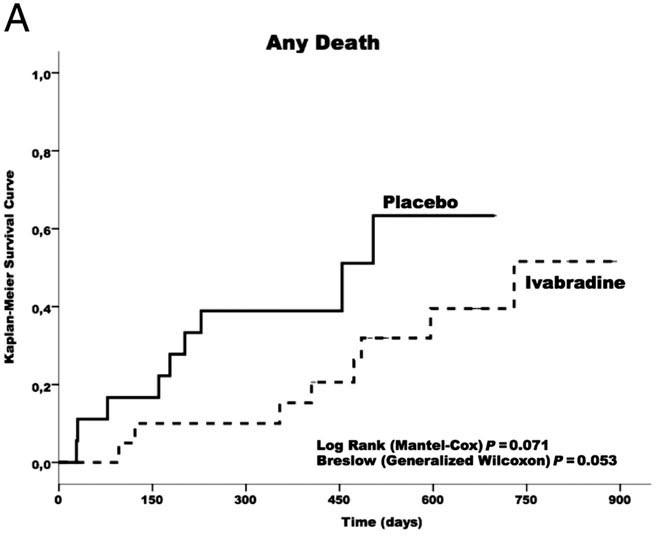
Figure 3. Kaplan–Meier survival curves free of any cause of death
The study concludes that ChD HF is known to be an advanced type of HF with poor prognosis. Ivabradine is significantly effective in reducing HR in ChD HF patients and improving functional class. However, it was suggested that Ivabradine may have a beneficial benefit–risk profile in these patients.

