The VICTORIA (Vericiguat Global Study in Subjects with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction) Trial
By: Paul Wayne Armstrong
Key Points
- Despite optimal guideline based treatment, patients with chronic heart failure (HF) have a substantial risk of death or HF hospitalization after a recent worsening HF event
- Vericiguat increases sGC activity to improve myocardial and vascular function
- The objective of the study was to assess whether vericiguat reduces the primary composite outcome of cardiovascular death or first HF hospitalization
- Secondary outcomes were:
- Components of the primary composite outcome
- Total HF hospitalizations; first and recurrent
- Composite of all-cause mortality or first HF hospitalization
- All-cause mortality
- Also, the safety and tolerability of vericiguat in this high risk population with HF with reduced EF (HFrEF) was evaluated
- VICTORIA enrolled a very high risk HF population with significant unmet needs not well addressed by prior HF studies
- Vericiguat engages a new therapeutic target by enhancing the cyclic GMP pathway
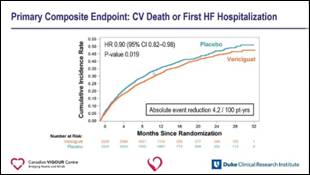
- Vericiguat achieved clinically meaningful absolute primary event reduction of 4.2/100 patient-years in the presence of guideline based care
- NNT for one year to prevent 1 primary outcome event is ~24 patients in this high risk HFrEF population followed for 10.8 months
- Because vericiguat is a once daily medicine, easy to titrate, generally safe and well tolerated, without the need for monitoring renal function or electrolyte, it may play a useful role in patients with a recent worsening heart failure event
Rivaroxaban for Prevention of Cardiovascular and Limb Events After Lower Extremity Revascularization: Primary Results of the Voyager Pad Randomized Trial
By: Marc P. Bonaca

Key Points
- The patients undergoing peripheral revascularization showed high risk of major adverse limb events and outcomes after hospitalization are poor with ~15% disabled or dead
- Despite the high risk, currently there is no proven antithrombotic strategy that has demonstrated efficacy for reducing major adverse limb and cardiovascular events after peripheral intervention for ischemia
- The objective of the study was to test whether rivoroxaban 2.5 mg twice daily added to low dose aspirin reduces the risk of major adverse limb and cardiovascular events compared to aspirin alone in PAD (Peripheral artery disease) patients undergoing lower extremity revascularization for ischemic symptoms
- And to evaluate the safety of rivaroxaban 2.5 mg twice daily added to low dose aspirin compared to aspirin alone
- In symptomatic PAD after revascularization, ~1 in 5 have acute limb ischemia, major amputation of vascular etiology, MI, ischemic stroke or cardiovascular death at 3 years
- Rivoraxaban 2.5 mg twice daily with aspirin compared to aspirin alone showed benefits apparent early and continued over time, consistent benefit across major subgroups and broad benefits including reductions in unplanned index limb revascularization
- In VOYAGER PAD, there was a numerical increase in TIMI major bleeding and significantly increased ISTH major bleeding but no excess in intracranial or fatal bleeding
- It prevents ~6 times as many ischemic events relative to bleeds caused in PAD patients after revascularization
Clinical Implementation of Clopidogrel Pharmacogenetics: The Tailor PCI Trial
By: Naveen L. Pereira
Key Points
- Clopidogrel is the most widely prescribed P2Y12 inhibitor after PCI
- TAILOR PCI trial was carried out to assess whether does identifying loss of function CYP2C19 allele carriers and altering P2Y12 inhibitor therapy based on CYP2C19 genotype reduce ischemic outcomes
- Tailor PCI study designed as a two arm, parallel, open label, international, multicentre, randomized superiority clinical trial and patients of ≥18 years of age who underwent PCI and needing 12 months of DAPT were included
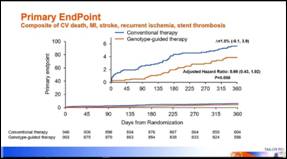
- Primary endpoint was the composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke, definite or probable stent thrombosis and severe recurrent ischemia within 1 year after index PCI
- Secondary endpoint was major or minor bleeding as defined by the TIMI criteria
- A genotype-guided oral p2Y12 inhibitor strategy compared with conventional clopidogrel therapy without point of care genotyping in CYP2C19 LOF patients with ACS and stable CAD undergoing PCI resulted in no significant difference in reducing ischemic events at 12 months based on the prespecified analysis plan and the 50% treatment effect that the study was powered to detect
- Potential benefit of genotype-guided therapy appears greatest within 3 months after PCI and for reducing multiple ischemic events per patient
Practice Factors Affecting Cardiologists’ Wellbeing: The American College of Cardiology 2019 Well Being Study
By: Laxmi S. Mehta

Key Points
- ACC survey data from 2015 showed that more than 1 crore US cardiologists and fellows in training were burnout where almost 50% were stressed and less than one quarter were not burned out and not highly stressed. The highest level of burnout was among midcore cardiologists
- The survey was sent to 19,348 ACC members in the 2019. 14,325 cardiologists were included in the survey and only 2,025 (14%) completed it
- The burnout was assessed by Mini Z survey which included questions regarding medical errors, desire to change jobs
- In 2019, >1/3 of US cardiologists reported being burned out – This has increased by 32% since 2015 and women and mid-career cardiologists are at higher risk of burnout
- Burnout rates are higher in cardiologists who work longer hours or in a hectic work environment, plan to leave current practice and among those reporting medical errors
- Among burned out cardiologist who plan to leave their job, desire to spend more time with family and work related factors (call, RVU, satisfaction scores) are frequently reported
Inclisiran Potently and Durably Reduces Ldl-c in A Pooled Analyses of Phase 3 Studies
By: R. Scott Wright
Key Points
- LDL-C lowering is the most effective intervention to change the course of ASCVD and FH yet substantial residual risk remains despite aggressive treatment with statins and other agents
- Ezetimibe and monoclonal antibodies to PCSK9 are adjunctive strategies to reduce LDL-C and clinical events by multiple treatment guidelines
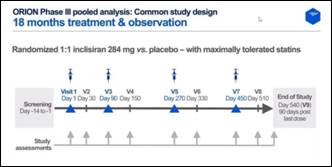
- The objective of the study was to assess efficacy and safety of Inclisiran 284 mg compared to placebo in a pooled analysis of all Phase III trials
- Patients were randomized 1:1 Inclisiran 284 mg vs. placebo with maximally tolerated statins
- The study has 2 core endpoints; The primary endpoint is changes in LDL-C vs placebo at day 510 and average reduction over days 90-540 and secondary endpoint is change in LDL-C over time and changes in PCSK9 and other lipids
- The safety and tolerability and exploratory endpoints (cardiovascular events) were also assessed
- Inclisiran is a novel approach to reduce the level of LDL-C
- With twice yearly administration, it provides robust and durable LDL-C reduction over 18 months on top of maximally tolerated oral therapies
- Effects were consistent in patients with heFH, ASCVD, or ASCVD risk-equivalence
- The safety profile was similar to placebo in a high risk population
- Twice yearly administration will coincide with typical twice yearly patients visits with health care providers, thereby assuring treatment adherence
Integrating The Effect of Polygenic Scores, Low Density Lipoproteins and Systolic Blood Pressure On the Lifetime Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
By: Brian A. Ference
Key Points
- The objective of the study to evaluate how much lifetime risk of cardiovascular disease varies at all levels of a polygenic score (PGS) for CAD depending on difference in lifetime exposure to low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and systolic blood pressure (SBP)
- To make inferences about how a PGS for CAD can be combined with information about LDL and SBP which are modifiable and the current targets of therapy to reduce risk
- To directly inform individual screening and treatment decisions
- To provide a potential framework for incorporating PGS for CAD into clinical medicine
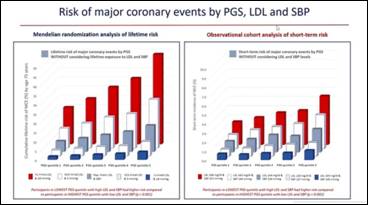
- 445,556 participants were enrolled in the UK Biobank and primary outcome i.e. major coronary event was assessed in 23,032 patients
- Lifetime risk of cardiovascular disease varies substantially at all levels of a polygenic score for CAD depending on differences in lifetime exposure to LDL and SBP
- Therefore, combining information about lifetime exposure to LDL and SBP with a PGS for CAD should more accurately estimate lifetime risk of cardiovascular disease, more accurately identify persons who may benefit from early interventions to reduce risk, and better estimate the potential benefit from early interventions because absolute lifetime risk of cardiovascular disease depends on PGS and lifetime exposure to LDL and SBP and clinical benefit depends on BOTH absolute risk and the absolute reduction in LDL or SBP achieved with treatment
- When combined with LDL and SBP, a PGS for CAD has the potential to help personalize the prevention of cardiovascular disease by helping to identify persons who may benefit the most from early interventions to minimize the cumulative effects of lifetime exposure to LDL and SBP
- This implies that the trajectory of cardiovascular risk predicted by a PGS can be reduced by lowering LDL and SBP
The Role of Combination Antiplatelet and Anticoagulation Therapy in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease: Insights from The Compass Trial
By: Deepak L. Bhatt
Key Points
- Prior ischemic events, stable cardiovascular disease increases CV death, MI, or stroke at 4 years as compared to patients with risk factors only
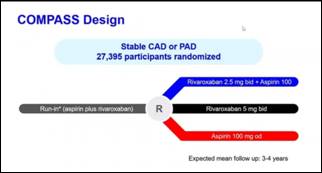
- In Compass trial, 27,395 patients with stable CAD (Coronary artery disease) or PAD (Peripheral artery disease) were randomized one of three treatments:
- Rivaroxaban 2.5 mg bid plus Aspirin 100
- Rivaroxaban 5 mg bid
- Aspirin 100 mg od
- The Compass diabetes analysis measured effects in patients with diabetes at baseline versus without diabetes and patients were randomized to rivaroxaban plus aspirin versus placebo plus aspirin
- Low-dose rivaroxaban plus aspirin reduce major CV events in stable atherosclerosis, irrespective of the presence or absence of diabetes, though absolte risk reductions were numerically larger with diabetes, including for all-cause mortality
- There was a significant increase in major bleeding, but not in fatal or intracranial bleeding
- The net clinical benefit when examining irreversible outcomes appeared numerically greater in those with diabetes
- Use of dual pathway inhibition with low-dose rivaroxaban plus aspirin is particularly attractive in high risk patients such as those with diabetes
Cost-effectiveness of Low-dose Colchicine After Myocardial Infarction in The Colchicine Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial (COLCOT)
By: Michelle Samuel
Key Points
- COLCOT is randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial in which 4,745 patients who had a myocardial infarction ≤30 days were enrolled and randomized 1:1 to low dose colchicine or placebo. Follow up was for 2 years
- Primary composite endpoints were death from cardiovascular causes, resuscitated cardiac arrest, myocardial infarction, stroke and urgent hospitalization for angina leading to revascularization
- The objective of the study was to assess the in-trial period and lifetime cost effectiveness of low dose colchicine compared to placebo in post MI patients on standard of care therapy
- From the Canadian healthcare system perspective, the addition of low-dose colchicine (0.5 mg daily) to standard of care therapy after MI is economically dominant
- Mean overall per patient costs reduced by 47% for the in-trial period and 69% for the lifetime period
- Quality adjusted life years (QALYs) increased
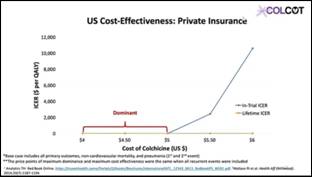
- From the US Medicare system perspective, low dose colchicine therapy post-MI was cost effective for the in-trial period and economically dominant at a price of <$5 per pill
- From the US private insurance system perspective, low dose colchicine post-MI was economically dominant at ≤$5 per pill for the in-trial period and $4-6 per pill for the lifetime period

