RIVAROXABAN VERSUS WARFARIN IN PATIENTS WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION AND VALVULAR HEART DISEASE: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS
Baral N, presented a study in a session at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 scientific sessions: virtual congress. Rivaroxaban is a non-vitamin k antagonist oral anticoagulant (NOAC) that is commonly used to treat non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation (AF). Besides that, there are still questions about its safety and effectiveness in patients with AF and valvular heart disease (VHD), which includes bioprosthetic valves.
A recent meta-analysis was performed to compare the effectiveness and safety of Rivaroxaban to Warfarin in patients with AF and VHD. A systematic study with meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and cohort studies reported until January 2021 was carried out. The following databases were searched: PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, Scopus (Elsevier), and the Cochrane database, which only included RCTs and cohort studies.
The quality of included studies and findings published using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) recommendations were assessed using the Downs and Black questionnaire method. Using Rev Man 5.4 software, a random-effects model was used to pool the data on effectiveness and protection using the hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI).
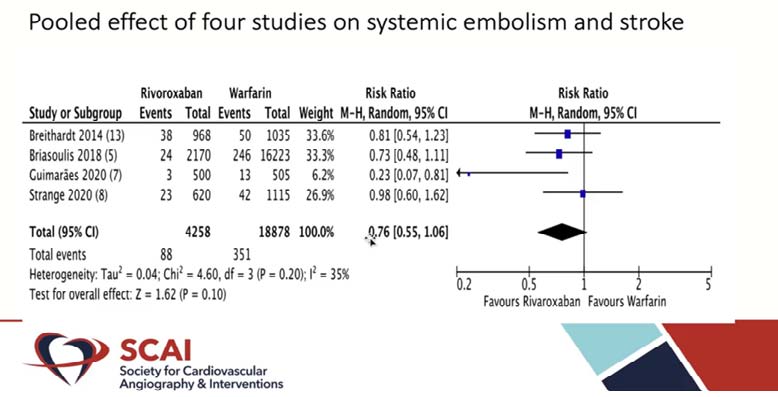
The pooled data from 4 studies showed stroke and systemic embolism in 88 of 4258 (2.06%) patients in the rivaroxaban group and 351 of 18878 (1.85%) patients in the warfarin group. The pooled result showed that the risk of stroke and systemic embolism was comparable across both groups (HR 0.76, 95%CI: 0.55-1.06; I = 35%). Rivaroxaban and warfarin were also associated with similar risks of intracranial hemorrhage (HR 0.49, 95% CI: 0.16-1.56; I = 70%) and major bleeding (HR 1.68, 95%CI: 0.59-4.77; I = 97%). Rivaroxaban and warfarin were both linked to similar risks of intracranial haemorrhage (HR 0.49, 95% CI: 0.16-1.56; I =70%) and major bleeding (HR 1.68, 95% CI: 0.59-4.77; I =97%).
In patients with AF and VHD, the findings indicate that rivaroxaban and warfarin have comparable efficacy and bleeding risks.
ONE MONTH VERSUS SIX TO TWELVE MONTHS OF DUAL ANTIPLATELET THERAPY AFTER PERCUTANEOUS CORONARY INTERVENTION WITH DRUG ELUTING STENT: A META-ANALYSIS OF RANDOMIZED CONTROL TRIALS
Bansal R, presented a study in a session at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 scientific Sessions: virtual congress. The new ACC/AHA/SCAI recommendations recommend dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) for 6 months after percutaneous coronary intervention in stable ischemic heart disease (SIHD) and 12 months in acute coronary syndrome (ACS) (PCI). A meta-analysis was performed to assess the optimal minimum length of DAPT after PCI with a drug-eluting stent (DES).
All studies comparing DAPT for 1 month vs. 6-12 months after PCI were included in the PubMed, Google Scholar, and Cochrane databases. One-year all-cause mortality was the primary endpoint of concern. The 1-year rates of stent thrombosis, bleeding, myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and target vessel revascularization (TVR) were the secondary outcomes. The Mantel-Haenszel random-effects model was used to measure pooled risk ratios (RR) and their respective 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
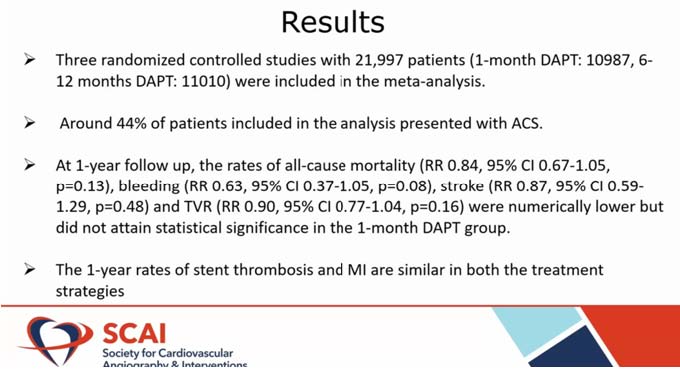
The meta-analysis involved three randomised clinical trials with a total of 21,997 participants (1-month DAPT: 10987, 6-12 months DAPT: 11010). About 44% of the participants in the study reported ACS. At one year, the rates of all-cause death (RR 0.84, 95% CI 0.67-1.05, p=0.13), bleeding (RR 0.63, 95% CI 0.37-1.05, p=0.08), stroke (RR 0.87, 95% CI 0.59-1.29, p=0.48), and TVR (RR 0.90, 95% CI 0.77-1.04, p=0.16) were numerically lower but did not achieve statistical significance in the 1-month DAPT group. The 1-year outcomes of stent thrombosis and MI in both therapeutic approaches are comparable.
Despite according to the findings, discontinuing DAPT after one month is a safe strategy following PCI.
INTAVSCULAR LITHOTRIPSY FOR TREATMENT OF SEVERELY CALCIFIED CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: THE DISRUPT CAD III STUDY AND BEYOND
Kereiakes DJ, presented a study in a session at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 scientific Sessions: virtual congress. Coronary calcification challenges have been documented. Increasing problem of the vascular calcium leads to calcium significant problem, limited tissue factor (TF) access due to calcium, below the knee (BTK) – Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) – critical limb ischemia (CLI) < 75% mod/severe calcium, coronary arteries ~2 m procedures < 25% mod/severe calcium, and iliac, femoral < 50% mod/severe calcium.
Impact of coronary calcification results in impedes device crossing, cause polymer delamination, stent under expansion, and alters drug elution kinetics. The larger the arc, volume, or thickness of calcium, the more likely the stent will expand. Asymmetrical stent expansion: up to 50% of stents deployed in calcified lesions. Stent under expansion and poor apposition: associated with increased ischemic events at 1 year. Primary safety endpoint includes freedom from major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) at 30 days – cardiac death, or myocardial infarction, or target vessel revascularization. Primary effectiveness endpoint includes procedural success – successful stent delivery with residual stenosis <50% and without in-hospital MACE.
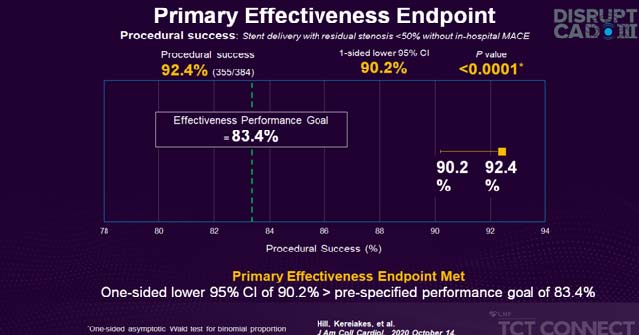
Primary safety endpoint met one-sided lower 95% CI of 89.9% > pre-specified performance goal of 84.4%. Primary effectiveness endpoint met one-sided lower 95% CI of 90.2% > pre-specified performance goal of 83.4%. Disrupt coronary artery disease (CAD) III intravascular lithotripsy (IVL) -induced ventricular capture reported 41% of patients with no sustained ventricular arrhythmias or clinical sequelae. Disrupt CAD III IVL learning curve reported that roll-in patients represent the first case for each site in the study. Baseline clinical and angiographic characteristics were similar between the two groups. Key study outcomes were similar between roll-in and pivotal patients
The Disrupt CAD III study was successful because both the primary protection and efficacy endpoints were reached during treatment with coronary IVL in severely calcified lesions. Coronary IVL was well received prior to drug-eluting stent (DES) implantation, with a low incidence of significant peri-procedural clinical and angiographic complications. Transient IVL-induced ventricular catch was normal, but it was always benign, with no clinical consequences in any of the patients.
Despite the fact that this research constitutes the first coronary IVL experience for US operators, high procedural performance and low angiographic complications were achieved, demonstrating the relative ease of use of IVL technology.
GLOBAL CASE-BASED SUMMIT: COMPLEX INTERVENTIONS WITHOUT BORDERS – LEFT MAIN CASE PRESENTATION
Alasnag M presented a case in a session at SCAI, 2021 Virtual Scientific Sessions. The case was of a 68 year old woman with recurrent rest angina. She was a known diabetes mellitus & hypertension patient. She had a history of Prior percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) of the left anterior descending artery (LAD) with a bio-absorbable scaffold following an acute coronary syndrome (ACS) at an outside facility 1 year ago.
Approach to treatment: Intracoronary imaging plays a crucial role in such cases to fully evaluate the case. PCI of mitral valve (MV) & bifurcation treatment strategy are the two treatment strategies. Bifurcation treatment strategy can be adopted in case small bowel (SB) needs to be preserved. Further, if chances of SB occlusion are high the procedure depends on SB angulation – T-stent, T and Protrusion (TAP) (70-900) or double kissing (DK) Crush, Culotte (<700). If chances of occlusion are low, provisional strategy may be adopted.
In complex distal LM bifurcations, SB lesion DS >70%; & OR length >10 mm; & OR SB right ventricular (RV) systolic dysfunction >2.5 mm with 2 stents – SB stent first & DK crush is recommended. DK crush provides the advantages of not losing wire in MB, with proper crushing optimal wiring can be performed with lower chances of wire going under the stent strut, final kissing can almost always be performed, ostium of SB is well covered, protects carina, chances of SB stent distortion are low & better outcomes than other bifurcation techniques.
Culotte technique is suitable for bifurcation lesion with two vessels of similar diameter; for all angles of bifurcations, especially when angle is ≤60 & it provides an optimal reconstruction of distal LM bifurcation with a significant area of stent overlap.
Treatment approach used was post-dilate, postural orthostatic tachycardia (POT), Re-wire LAD & open struts. Both the vessels were wired & circle flex coronary arteries were ballooned. The stent was deployed & while kissing the stent slipped. The kissing was performed with noncompliant balloons at intermediate atmospheres & subsequently proximal optimization was done.
The patient of recurrent rest angina was successfully managed with DK crush technique.
ONE MONTH DUAL ANTIPLATELET THERAPY AFTER PERCUTANEOUS CORONARY INTERVENTION WITH DRUG ELUTING STENT IN HIGH BLEEDING RISK PATIENTS: A POOLED ANALYSIS
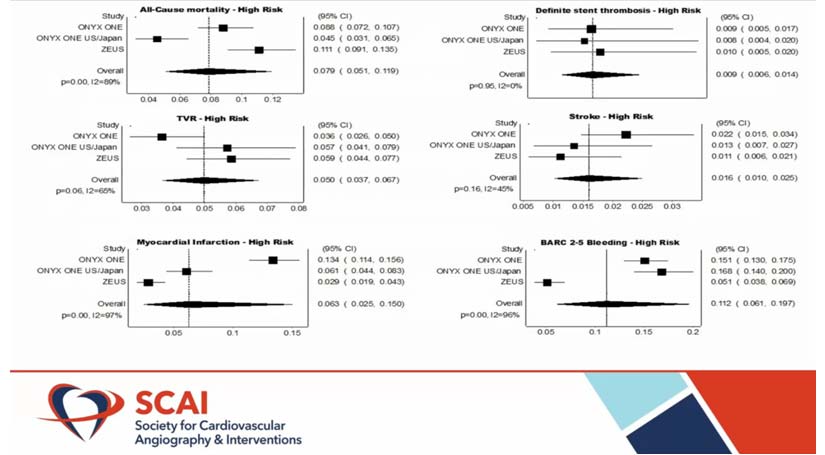
Thandra A, presented a study in a session at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 scientific Sessions: virtual congress. According to ACC/AHA/SCAI guidelines (class IIb), it is appropriate to discontinue dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) after 3 months in patients with high bleeding risk (HBR-which involves advanced age >75 years, anaemia, thrombocytopenia, previous bleeding, recurrent NSAID use, and so on) who had percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with drug eluting stent (DES). A meta-analysis was performed to determine the safety and efficacy of 1-month DAPT.
Both reports documenting outcomes of 1-month DAPT therapy after PCI with polymer-based DES stents were searched in PubMed, Google Scholar, and Cochrane databases. The primary outcome of concern was all-cause mortality after one year. The 1-year rates of stent thrombosis, myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and target vessel revascularization (TVR) were secondary outcomes.
The random-effects model was used to measure pooled prevalence with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The pooled research involved three trials of a total of 2,385 HBR patients with an average age of 73 years.
About 53% of the patients involved in the study had acute coronary syndrome (ACS). At one year, the pooled rate of all-cause mortality was 7.9% (95% CI: 0.058-0.12), and MI was 6.3% (95% CI: 0.023-0.14). The estimated pooled frequency for stent thrombosis, TVR, and stroke was 0.9%, 5%, and 1.6%, respectively. In comparison, the bleeding academic research consortium (BARC) 2-5 bleeding rate was 11.2%.
The study revealed adequate 1-year mortality rates in this high-risk population, as well as lower rate of stent thrombosis and TVR. As a result, discontinuing DAPT after one month in HBR patients is a healthy and successful approach.
LONG-TERM ISCHEMIC AND BLEEDING RISK WITH EXTENDED DUAL ANTIPLATELET THERAPY AFTER PCI IN PATIENTS WITH 2018 ESC/EACTS MYOCARDIAL REVASCULARIZATION GUIDELINE-ENDORSED HIGH ISCHEMIC RISK FEATURES
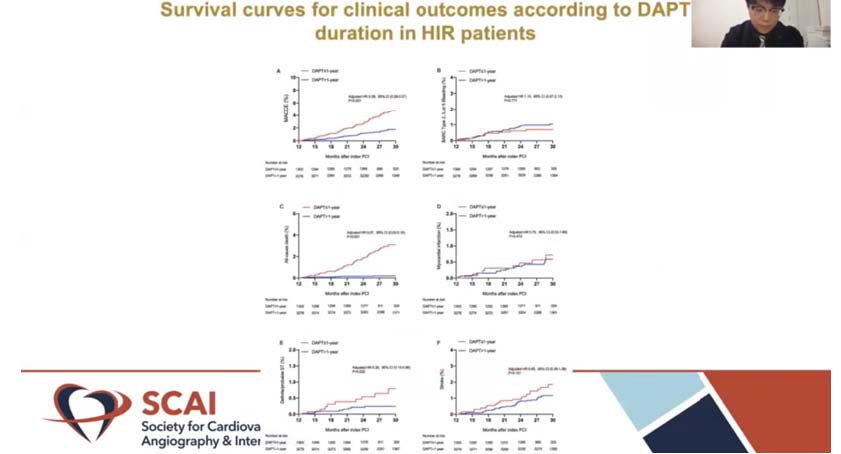
Wang H, presented a study in a session at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 scientific Sessions: virtual congress. The ischemic/bleeding trade-off of prolonged dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) after PCI for patients with high ischemic risk (HIR), as recommended by the 2018 ESC/EACTS myocardial revascularization guidelines, is still unclear. The aim of this study was to compare the benefits and harms of DAPT with duration of more than one year versus DAPT with duration of one year on long-term clinical results after PCI with DES in ESC/EACTS guideline-endorsed HIR patients.
Patients from the prospective Fuwai registry who underwent coronary stenting between January 2013 and December 2013 were described as HIR if they met at least one ESC/EACTS guideline-endorsed HIR criteria and had at least one of the following characteristics: diffuse (lesion length 20mm) multivessel disease in diabetic patients, CKD (eGFR 60 mL/min), ≥ 3 stents implanted, ≥ 3 lesions treated, bifurcation with 2 stents implanted, total stent length > 60 mm, treatment of CTO, and history of STEMI. A total of 4578 patients were examined who were at HTR who had no accidents one year after PCI. Significant adverse heart and cerebrovascular effects is the major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE).
> 1-year DAPT of clopidogrel and aspirin significantly decreased the risk of MACCE relative to 1-year DAPT (1.9% vs. 4.6%; HR: 0.38; 95% CI:0.27–0.54; p < 0.001), led by a decrease in all-cause mortality (0.2% vs. 3.0%; HR, 0.07; 95% CI,0.03–0.15). Cardiac mortality and definite/probable stent thrombosis were also less common in the sustained DAPT community. Both participants experienced comparable rates of BARC form 2, 3, or 5 bleeding (1.1% vs. 0.9%; HR, 1.11; 95% CI, 0.58–2.13;
p = 0.763). Analyses of the multivariable Cox construct, likelihood score matching, and reciprocal likelihood of treatment weighting yielded similar outcomes.
Continued DAPT beyond 1 year could provide better efficacy in terms of atherothrombotic events and comparable protection in terms of clinically significant bleeding. The ESC-HIR criterion is a crucial factor to consider when tailoring DAPT prolongation.
CALCIFIED LESIONS CASE PRESENTATION
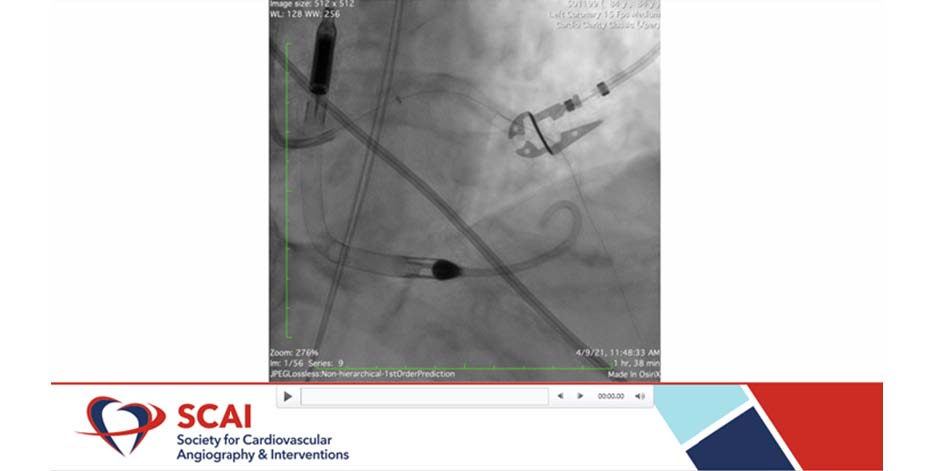
Nguyen J, presented a case in a session presented at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 scientific sessions: virtual congress. The case was of an 86-year-old male came for mitral clip workup. He had worsening sob over several months. An echocardiogram showed an ejection fraction (EF) of 20-25% with severe mitral regurgitation. CT surgery was called for evaluation for bypass surgery and mitral valve repair. However, the patient developed acute chest pain overnight with hypotension. Laboratory investigation showed that patient’s blood pressure (BP) was 87/43 and heart rate (HR) was 78.
At first, a surgery was declined to the case stating that the patient was too unstable. Thus, only lifesaving measure was percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for the patient. The risk of the procedure was explained to the family members and they agreed to proceed the procedure. Impella device inserted prior to start of the case. Whisper wire was advanced into the distal left anterior descending artery (LAD). Whisper wire was then replaced with rota floppy wire. A 1.25 burr was used for multiple runs of rotational atherectomy.
Balloon angioplasty was done using 2.5×20 mm balloon inflated to 20atm. Difficulty advancing stent and balloon angioplasty done again with 3.5x20mm balloon. Stented left main to mid LAD with a 4.0x30mm drug-eluting stent (DES) and 3.0×40 mm DES and post dilation done with a 4.0×20 mm noncompliant (NC) balloon. Following the surgery, patient’s chest pain was subsided and BP was improved to 126/78. Patient showed well recovery and was discharged in stable condition on day 7 post PCI.
The patient with mitral regurgitation was auspiciously managed with balloon angioplasty and DES.
DRUG-COATED BALLOON & DRUG-ELUTING STENT: WHERE SHOULD WE USE IT IN 2021?
Secemsky EA, presented a study in a session at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 scientific sessions: virtual congress. According to the CCI 2011 study, superficial femoral artery (SFA) patency decreases with increasing lesion length. In several studies i.e. FAST, RESILIENT, ASTRON, ABSOLUTE, uncoated percutaneous transluminal balloon angioplasty (PTA) was performed with provisional stent while Zilver PTX study, paclitaxel-coated drug-eluting stents were used in PTA.
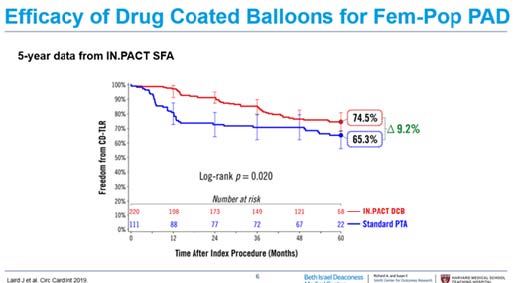
The drug-coated balloon (DCB) arm of the RCTs showed a significant advantage in target lesion revascularization (TLR) compared with plain old balloon angioplasty (POBA) at 2 years (OR, 0.29; 95% CI, 0.20-0.40). While in another study, drug-eluting stent (DES) exhibited benefits in TLR/TVR (OR,0.55 CI, 0.41-0.72). 5-Year data of Zilver PTX RCT showed that patients with symptomatic femoropopliteal artery disease were randomly assigned to Zilver PTX DES or PTA. PTA patients randomized to BMS or Zilver PTX. The 5-year primary patency rate for the overall DES group was superior to the standard care group (66.4% vs 43.4%, p<0.01). Primary patency rates were 83% for DES, 77.1% for DCS in zilver PTX RCT, 78.9% for DCB in IN.PACT SFA study. 2018 SCAI Consensus Guidelines for Fem-Pop PAD recommended IIA treatment for CDB and IIA and IIB for DES.
The Vascular Quality Initiative (VQI) registry from 2010–2017 for all peripheral vascular interventions (PVI) involving the SFA showed that Primary treatment utilization changed from 40% balloon angioplasty, 45% stenting, and 15% atherectomy in the PRE era to 22% POBA, 26% BMS, 8% atherectomy, 37% DCB, and 8% DES in the POST era (p < .001). Paclitaxel works as evidence supporting superiority over uncoated devices to 5 years with complex lesions, long lesions, CTOs. Paclitaxel was frequently used up to the time of the Katsanos meta-analysis.
Paclitaxel is recommended as definitive therapy in most SFA lesion subtypes. Recent observational and randomized trial data have supported safety of paclitaxel-coated devices. Thus, risks/benefits of therapy and document/consent should be considered until FDA updates the health provider letter.
OUTCOMES ASSOCIATED WITH NSTEMI IN PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOSIS: ANALYSIS OF THE NATIONAL INPATIENT SAMPLE 2016-2018
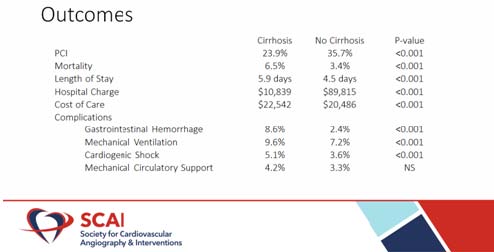
Thandra A, presented a study in a session at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 scientific Sessions: virtual congress. Cirrhosis has a significant effect on coagulation, hemodynamics, and inflammation in patients with cardiovascular disease. Cirrhosis, on the other hand, has a less direct effect on outcomes and resource use in non-ST segment myocardial infarction (NSTEMI).
The ICD-10 classification was used to identify patients admitted specifically for NSTEMI in the 2016-2018 National Inpatient Sample (NIS). NIS is an all-payer inpatient database that estimates 37 million hospitalizations in the United States per year. Clinical results were adjusted for demographics, comorbidities, and risks using multivariate hierarchical regression analysis.
Cirrhosis was found in 12,150 of the 1,405,589 patients admitted for NSTEMI. Cirrhotic patients were more likely to be male (64.2% vs. 59.8%, p<0.001) and Hispanic (12.4% vs. 8.7%, p<0.001). Utilization of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) (23.9% vs. 35.7%, p<0.001) and drug-eluting stents (20.0 vs. 33.2%, p<0.001) were lower among cirrhotics. Cirrhotic patients have higher rates of gastrointestinal haemorrhage (8.6% vs. 2.4%, p<0.001), thrombocytopenia (30.4% vs 5.1%, p<0.001), and cardiogenic shock (5.1% vs. 3.6%, p<0.001), as well as needing more transfusions (12.8% vs 5.7%, p<0.001) and breathing (9.6% vs. 7.2%, p<0.001).
Despite lower rates of percutaneous revascularization, the prevalence of cirrhosis greatly raises complications and mortality in patients admitted for NSTEMI. These findings justify the inclusion of comorbid liver disease in NSTEMI risk stratification and evaluation.
EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF INTRACORONARY TRANSPLANTATION OF PERIPHERAL BLOOD- DERIVED MONONUCLEAR (PBMNCS) AUTOLOGOUS STEM CELLS IN PATIENTS WITH ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION: IST PILOT STUDY FROM NORTH INDIA (ITPASC STUDY)
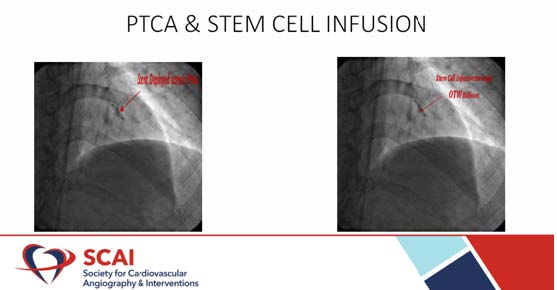
SHOWKAT HI, presented a study in a session at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 scientific Sessions: virtual congress. It is a prospective pilot study with a six-month follow-up period. 10 ST-high ST acute prior wall patients before the coronary operation, myocardial infarction with left anterior descent occlusion was taken for echocardiogram.
The drug eluting stem, accompanied by the intracoronary infusion of peripheral blood- derived mononuclear (PBMNCS), percutanically performed coronary operation of left anterior descending (LAD). A monitoring was provided in 10 patients with acute myocardial anterior wall infarction, in which only LAD stenting was performed. The suspension of PBMC has been remotely infused through the centre port of the balloon catheter with the occluding ball and has been replicated 4 times to enable the infusion of a complete cell suspension of 20 ml disrupted by 2-3 minutes. Until intracoronary cell transplantation, echocardiography was performed by blinded operators.
There were equivalent demographic factors, therapeutic variables and left ventricular systolic functions at the baseline. The left ventricular function was improved after six months of follow-up in both case and control. But in the case of intracoronary stem cell therapy in addition to LAD stenting, improvement is achieved in the left ventricular system compared with a placebo sample in which only LAD stenting has been carried out. A statistically meaningful increase in the ejection fraction and wall movement score index (p <0.05) in the stem cells treatment community was observed.
Intracoronary PBMNCs infusion is a less invasive, more feasible, safer and a novel therapy for acute myocardial infarction patients who have depressed cardiac function. It causes significant improvement in parameters of left ventricular functions especially Ejection fraction and wall motion score index which are most important prognostic factor in myocardial infarction patients.
ADVANCED CUSP OVERLAP CASE—BICUSPID ANATOMY
Grubb KJ, presented a case study in a session at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 scientific sessions: virtual congress. A 65 year old female presented with worsening shortness of breath and lower extremity oedema. Her past medical history included severe Bicuspid AS (Sievers 0); atrial fibrillation (on Xarelto); moderate mitral regurgitation; moderate to severe tricuspid regurgitation; moderate pulmonary insufficiency; OA awaiting knee replacement & obesity (BMI 34). Heart Team – Intermediate to High Risk; No Society of Thoracic Surgeons Predicted Risk of Mortality (PROM) for multivalve. ECG was abnormal & positive for AF and had low voltage QRS complex.
The Heart Team discussed over Sievers 0 Bicuspid; bulky annular calcium into the LVOT showing concern for PVL, risk of annular rupture & risk of pacemaker. The patient also had a large annulus – treatment 26 S3 Ultra vs. 34 Evolut Pro+ The team concluded on proceeding with 34 Evolut Pro+ with Predilation 20mm True balloon.
Pre-surgery: Protamine was infused to reverse heparin. Surgical procedure was taken ahead with Hybrid Cath Lab, nurse led sedation without anesthesiologist, perfusionist, or OR team. Radial access for CEP; Bilateral femoral arterial; 2 Perclose for large sheath (Ultrasound and fluoro guided); Single venous sheath as central line and TVP & was proceeded through fast-track pathway with possible same day discharge. Lunderquist Guidewire was confirmed in LV Apex with TTE. It was start mid-pigtail allowing the valve to descend into the annulus. Final Angiogram revealed 1mm on NCC & 3mm on LCC. Post TAVR Echocardiogram was performed. The patient was discharged with instructions reviewed by patient and care partner 6 hours after Trans-catheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
The patient with aortic valve stenosis was successfully managed with Trans-catheter aortic valve replacement.
THE HARMONY TRANS-CATHETER PULMONARY VALVE: 1-YEAR OUTCOMES FROM THE PIVOTAL TRIAL AND 30-DAY OUTCOMES FROM THE CONTINUED ACCESS STUDY

Jones TK, presented a study in a session at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 scientific Sessions: virtual congress. The Medtronic Harmony Trans-catheter Pulmonary Valve (TPV) was recently approved by FDA for the treatment of severe pulmonary regurgitation (PR).
Results from Pivotal Trail demonstrated favorable clinical and hemodynamic outcomes in the TPV22 and TPV25 devices over 6 months were presented. The study reported the combined 1-year results from the Pivotal Trial and the early results from the Continued Access Study for the safety and efficacy of the Harmony TPV system. 68 patients with Severe PR by echo OR PR fraction ≥ 30% by CMR were included in the trial.
The results demonstrated that >90% of patients had none/trace PR at all follow-up visits. No explants, endocarditis, major stent fractures, thrombosis, or death was observed. Several patients had stable non-sustained ventricular tachycardia after implant that resolved which was not found to be clinically significant.
In patients requiring a surgical placement of Right ventricular pulmonary artery (RV-PA) conduit or prosthetic pulmonary valve, Harmony Trans-catheter Pulmonary Valve appears to be safe and effective option.
IV PLATELET INHIBITION DURING HIGH-RISK PCI: WHICH PATIENTS BENEFIT THE MOST?
O’Donoghue ML, presented a study in a session at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 scientific Sessions: virtual congress. The aim of this prospective, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel design analysis was to compare the effects of cangrelor vs placebo on in patients undergoing P-PCI (n=50) who were also receiving crushed ticagrelor.
Randomization took place after angiography or a STEMI diagnosis indicated PCI suitability. Medication for the double-blind trial was provided as soon as possible after randomization. The prescribing physician had the option of continuing the study drug infusion (cangrelor or a matching placebo) for another 2-4 hours. Patients were switched to replacement clopidogrel treatment after receiving a loading dose of clopidogrel or a matching placebo at the end of the infusion.
The investigator directed that the clopidogrel loading dose (or a corresponding placebo) be administered. The investigator indicated a clopidogrel loading dosage of 600 mg or 300 mg at the time of patient randomization.
Cangrelor shows 4.7% lesser event rate of death/MI/IDR/stent thrombosis within 48 hours vs. 5.9% with Clopidogrel. Cangrelor shows 0.8% lesser event rate of stent thrombosis within 48 hours vs. 1.4% with Clopidogrel. When compared to clopidogrel + GPIs, cangrelor alone was associated with similar ischemic risk and lower risk-adjusted significant bleeding risk.
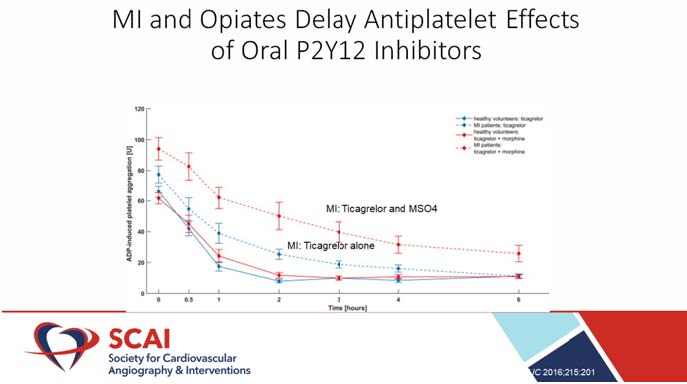
At the time of randomization, both patients were receiving 180mg LD crushed ticagrelor (time 0) PCI is completed in 41 (21-54) minutes. Cangrelor greatly reduced PRU levels at 30 minutes (primary end point) as compared to placebo [63 (32-93) vs. 214 (183-245); mean difference: 152; 95 percent CI: 108-195; p0.001]. Antiplatelet symptoms of oral P2Y12 inhibitors are delayed, which is exacerbated in the presence of MI and/or opiates. Cangrelor is a parenteral P2Y12 receptor blocker that has a quick onset and offset kinetics. Cangrelor lowers the risk of periprocedural ischemic attacks without raising the risk of serious bleeding.
In conclusion, the efficacy and safety of Cangrelor is consistent irrespective of high-risk features and use of a GPI.
ASIAN INVASIVE RISK PROFILE FOR CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: THE AIR CAD STUDY
Sedhom R, presented a study in a session at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 scientific sessions: virtual congress. This study was conducted to examine and compare the metabolic risk profiles of people of South Asian (SA), Middle Eastern (ME), and East Asian (EA) descent who had coronary angiography for angina or acute coronary syndromes (ACS).
Between January 2010 and January 2019, a retrospective study was conducted on patients who registered as having SA, ME, or EA ethnic backgrounds. Data on metabolic risk profiles were collected at the time of admission for elective coronary angiography or urgently for ACSs, as well as a comparison of quantitative coronary analysis (QCA) and intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) measurements.
The average age of the SA group was 62.2 (n=78), the ME group was 59.8 (n=24), and the EA group was 68.9 (n=112), with the male gender predominating (49 [62.8%] SA): (19 [79.2%] ME): (77 [68.8%] SA). The majority of the patients had ACS, with 51.3% having SA, 70.8% having ME, and 55.4% having EA. ME had the maximum mean TC rating at 170.55, followed by SA at 165.91, and EA at 153.17. Mean low-density lipoprotein cholesterol test (LDL-C) (101.95 ME, 93.78 SA, and 91.75 EA) and mean HDL-C (101.95 ME, 93.78 SA, and 91.75 EA) followed a similar pattern (39.09 ME, 39.45 SA, and 40.26 for EA). Mean TGs, on the other hand, is slightly higher for SA (169.25), 165.23 for ME, and lowest (126.84) for EA (p=0.048).
The development of targeted dietary, medicinal therapy, environmental, and psychosocial programmes to fit the needs of individual patient groups for disease prevention and related adverse health effects can be improved by research into the metabolic risk profile and coronary artery disease burden of people of various ethnic backgrounds.
LEADING THE WAY IN HIGH BLEEDING RISK PATIENTS: OLD SURGERY – NEW QUESTIONS
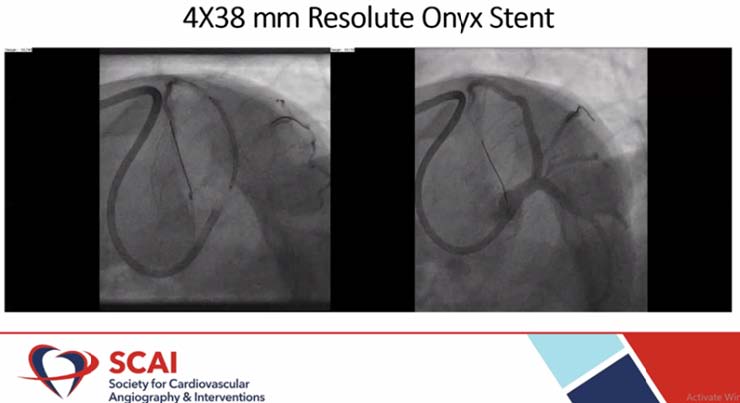
Mondal PC, presented a study in a session at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 scientific Sessions: virtual congress. The case was of 58-year-old non-diabetic, non-hypertensive, ex-smoker presented with on and off chest pain for 2 days. He was known patient of cirrhosis of liver with history of GI bleeding. ECG showed dynamic ST-T changes in leads V2-V6. Echo showed hypokintic IVS and anterolateral LV free wall with normal wall thickness and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) 48%. His BMI was 18.5, Hemoglobin 9.8 gm%. LFT showed raised SGPT and Alk phos. Coronary angiogram (CAG) was done which showed blood flows through the heart. Left anterior descending (LAD) stenting was performed with BMW wire. Sion blue wire was used at LAD-D1 and 3×12 maverick balloon at 12 atm. Recent published randomized controlled trial data show that the drug-coated balloon (DCB) technique with optimal lesion preparation, functional testing, use of antiproliferative drugs to inhibit intimal hyperplasia, and short-term dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) has become a valid option for the treatment of coronary artery disease in many clinical situations. Although DCBs are an established therapeutic option for the treatment of ISR supported by guideline recommendations, a DCB-only approach in de novo lesions of coronary small-vessel disease is now a valid treatment alternative to drug-eluting stent (DES) if current recommendations regarding optimal balloon angioplasty and subsequent DCB delivery are adequately followed. In ZEUS study, Zotarolimus-eluting Endeavor Sprint stent as compared with bare metal stent reduces major adverse cardiovascular event, myocardial infarction, target vessel revascularization, stent thrombosis.
4X38 mm Resolute Onyx stent was placed in the patient. New DES platforms have enhanced safety engineering with biocompatible durable polymers. Resoulte Onyx stent is a single wire design with platinum iridium core and biolinx polymer. Biofreedom DCS is the only available DES recommended by the ESC guidelines for high bleeding risk (HBR) patients with 1-month DAPT. According to Onyx one study, Resolute Onyx is safe and effective in complex high bleeding risk patients with 1-month DAPT. Patient recovered well and discharged in stable condition on day 7 post percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI). The follow up treatment was Ecosprin 75 mg OD, Clopidogrel 75 mg OD, Atorvastatin 20 mg OD and Propanolol 10 mg TID.
The HBR patient was successfully managed with Resolute Onyx DES with 1-month DAPT.

