This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluates the effectiveness of pulmonary artery pressure (PAP)-guided management using the CardioMEMS Heart Failure System in patients with heart failure (HF) outside the controlled settings of randomized clinical trials. The study aims to assess real-world evidence regarding the system’s impact on key clinical outcomes, particularly heart failure hospitalizations (HFHs), functional status, and quality of life.
Researchers conducted a comprehensive literature search across PubMed, ClinicalTrials.gov, and the Cochrane Clinical Trial Collection up to January 8, 2025. The inclusion criteria specified adult patients with HF who had undergone pre/post comparisons after CardioMEMS implantation, with at least six months of follow-up and available data on HFH rates. Eight studies met the criteria, encompassing 3,306 patients, with equal representation from the US and Europe. Half of the studies were single-arm and industry-funded, while the remaining were based on real-world clinical practice.
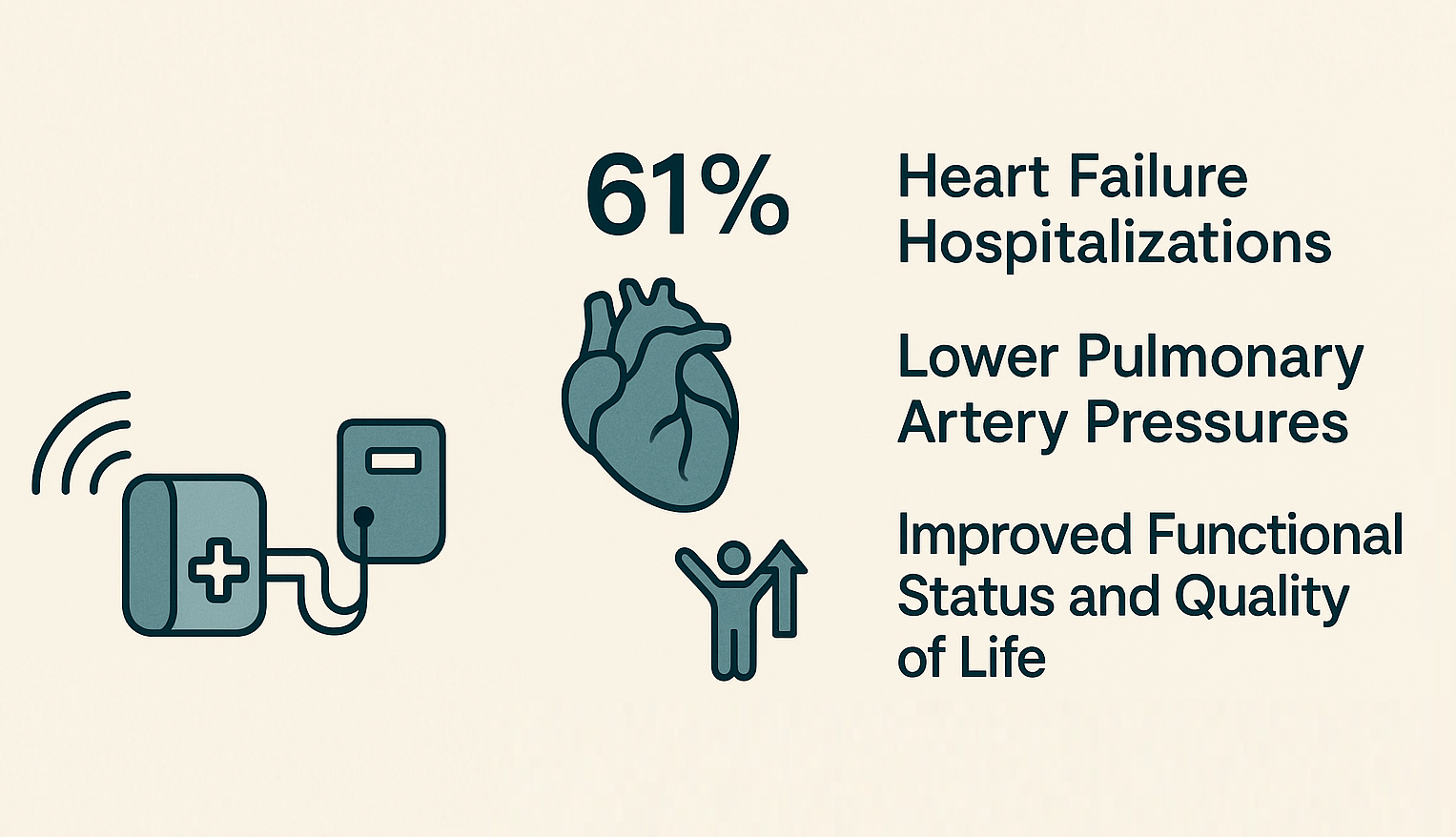
Results indicated statistically significant reductions in systolic (−7.8 mmHg), mean (−5.2 mmHg), and diastolic PAP (−4.4 mmHg) following device implantation. Additionally, there was a marked improvement in patients’ New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class, with 56% categorized as Class I/II one year post-implantation. Quality of life, assessed via the EQ-5D-5L visual analogue scale, also showed notable improvement.
Most strikingly, the intervention was associated with a 61% reduction in HFHs at the one-year mark (incidence rate ratio of 0.39). These outcomes suggest that PAP-guided management with CardioMEMS significantly benefits HF patients in everyday clinical settings, offering a reduction in hospital admissions, enhanced hemodynamic stability, and better overall patient well-being.
In conclusion, this review underscores the effectiveness of CardioMEMS in improving real-world outcomes for HF patients, supporting its broader adoption beyond clinical trial environments. The findings highlight its potential as a valuable tool for clinicians in tailoring proactive, data-driven HF management strategies.
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ejhf.3687

