
Introduction to Diabetes Distress:
Addressing the emotional side of diabetes and its management has received considerable attention in recent years. At the centre of most of these efforts is the concept of ‘diabetes distress’, a generic term that captures the primary sources and intensity of emotional distress associated with diabetes and its management over time. Karin Kanc discussed the recommendations for the clinical management of diabetes distress. The findings were presented at the EASD Annual th st Meeting 2025, held from 15 -19 September 2025 in Vienna, Austria.
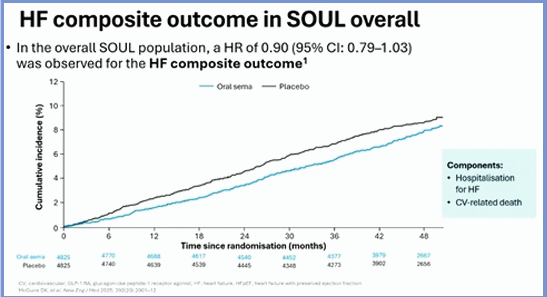
In clinical trials, once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide reduced the risk of HF outcomes compared with placebo in individuals with HF (including those with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), obesity or chronic kidney disease). Data to benchmark results, in patients with cardiometabolic HFpEF semaglutide and tirzepatide showed >40% risk reduction for the composite of hospitalisation for HF or all-cause mortality compared with a placebo proxy. Rodica Pop-Busui aimed to assess the effects of oral semaglutide on heart failure outcomes in SOUL. The findings were presented at the EASD Annual th st Meeting 2025, held from 15 -19 September 2025 in Vienna, Austria.
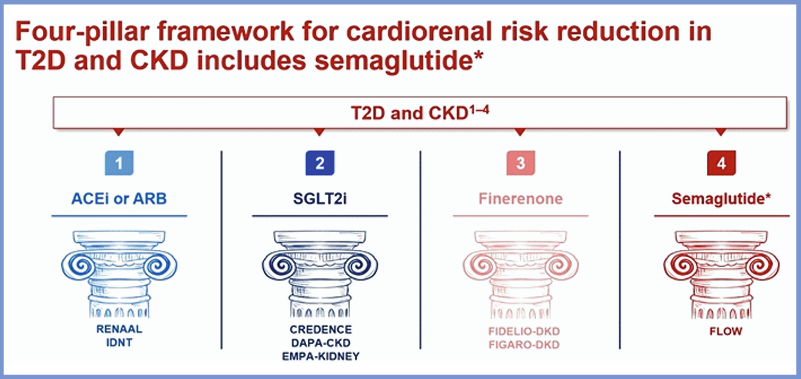
Diabetes is the leading cause of CKD and kidney failure. ~40% of people with T2D develop CKD. The risk of CV mortality increases with increased CKD staging, regardless of diabetes status. Paola Fioretto assessed the role of GLP-1RAs in the CKD and T2D nexus. The findings were presented at the th st EASD Annual Meeting 2025, held from 15-19 September 2025 in Vienna, Austria
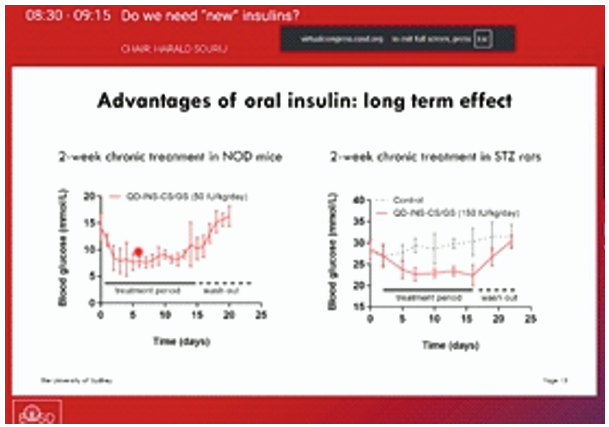
Insulin is highly sensitive to degradation from stomach acid and enzymes, but quantum dot (QD) conjugation can help make it insoluble across a wider pH range. While QD-insulin conjugation improved stability, QD-insulin alone was not effective in mice studies. The findings were presented at the EASD Annual Meeting 2025, held from 15 -19 September 2025 in Vienna, Austria.
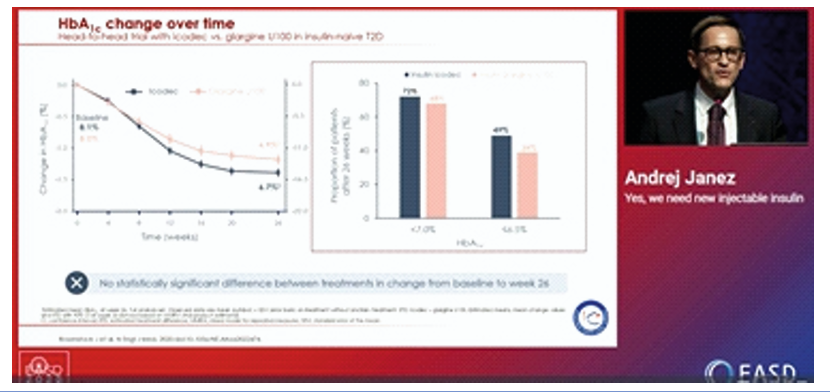
Insulin is the oldest of the currently available diabetes medications, has the most clinical experience. It is the most effective agent when used in adequate doses to decrease any level of HbA1c to the therapeutic goal. The updated ADA/EASD consensus recommends the use of GLP-1 receptor agonists or SGLT2 inhibitors with proven cardiovascular benefit in patients with type 2 diabetes and established ASCVD or high cardiovascular risk. Several studies have stated that initiation of insulin therapy is often delayed, leading to an increased risk of complications in patients with diabetes. The findings were presented at the EASD
Annual Meeting 2025, held from 15 -19 September 2025 in Vienna, Austria.
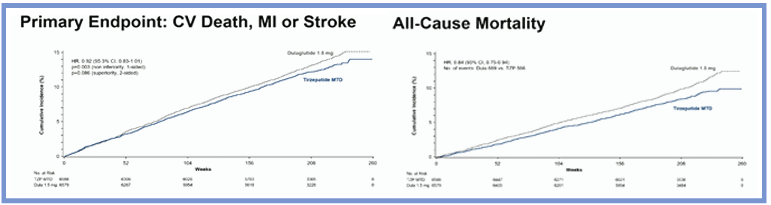
Tirzepatide, a dual GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonist, has been shown to improve glycaemic control and promote weight loss when compared with selective GLP-1 receptor agonists. Benefits of tirzepatide have also been observed for atherogenic lipoproteins, blood pressure, high sensitivity C-reactive protein and kidney function in comparison with selective GLP-1 receptor agonists or basal insulins. Stephen Nicholls assessed the cardiovascular outcomes in participants on tirzepatide versus dulaglutide in the SURPASS-CVOT trial. The findings were presented at the EASD Annual Meeting 2025, held th st from 15- 19 September 2025 in Vienna, Austria.







