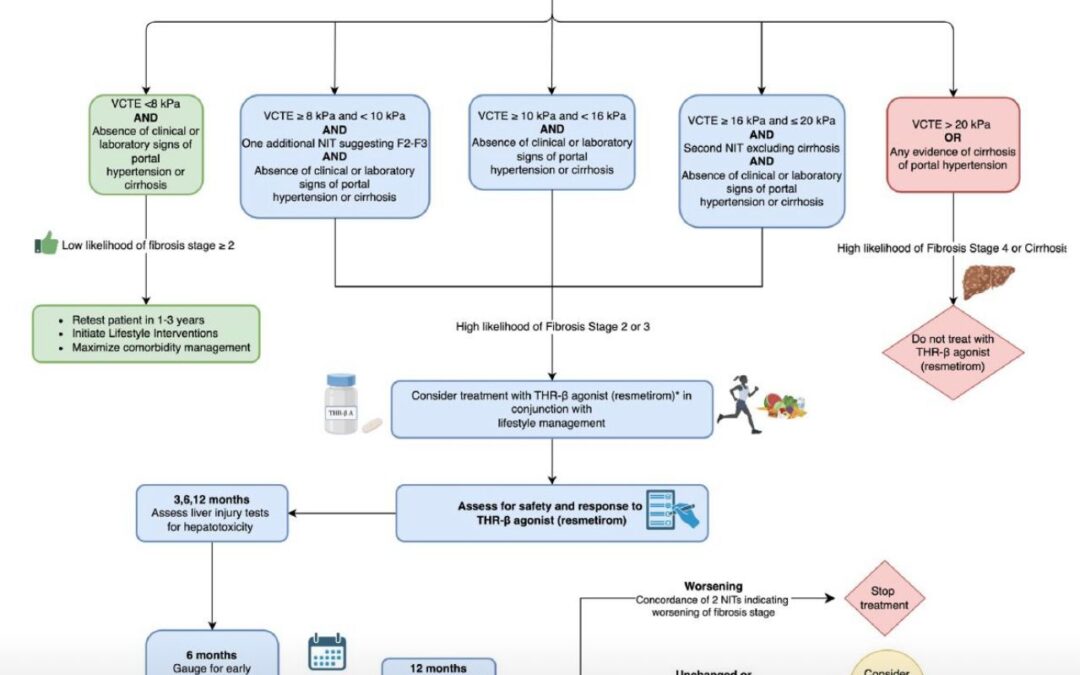
The Global Consensus Recommendations for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH), represent a landmark effort by an international multidisciplinary panel of 50+ experts from hepatology, endocrinology, and primary care. Developed via a two-round modified Delphi process (87% agreement threshold) and systematic literature review (up to May 2024), these guidelines update prior NAFLD/NASH frameworks to align with the 2023 nomenclature shift, focusing on cardiometabolic drivers to enhance diagnostic precision and therapeutic equity.

The World Health Organization (WHO) has published its first global guideline on managing sickle cell disease (SCD) during pregnancy—marking a critical step in addressing the serious health risks this condition poses for both mothers and babies. SCD, a group of inherited blood disorders, causes red blood cells to become abnormally shaped, leading to complications such as severe anemia, pain crises, infections, and life-threatening events like strokes and organ failure.
This case report details an extremely rare disease called drug-induced immune hemolytic anemia (DIIHA) that developed in a 52-year-old man once he started using the drug dapagliflozin (Farxiga), a drug often prescribed for diabetes. The report speculates that this could be the first to link this particular drug to this unusual disorder. DIIHA is a dangerous side effect wherein the immune system abnormally reacts against and destroys red blood cells upon exposure to a drug. While extremely uncommon, affecting 1-2 people per million individuals per year, it is life-threatening unless treated.

The American Gastroenterology Association (AGA) has provided updated guidelines for managing hepatitis B virus reactivation (HBVr) in at-risk individuals. The guidelines focus on preventive strategies and monitoring approaches based on patient risk levels.





