Off-Label Rituximab for Systemic Autoimmune Diseases: A Case Series
from a Third Level Hospital during a 5 Year- Period
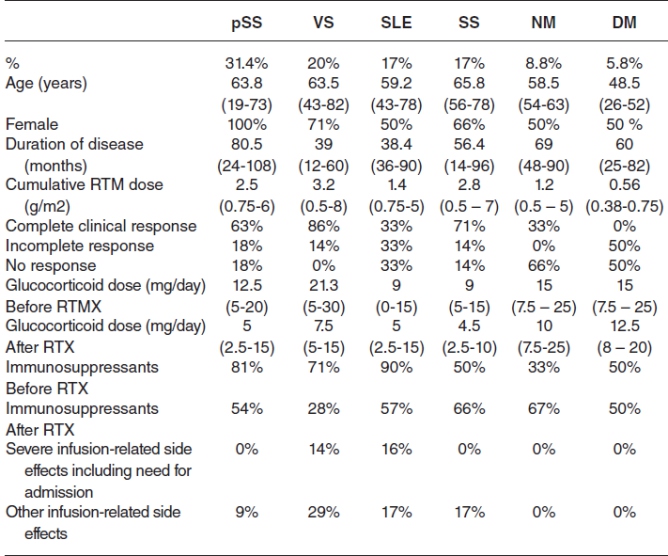
Santos CS, presented a study in a session at the European congress of rheumatology (EULAR) 2021 scientific sessions: virtual congress. Patients with SAD who had been treated with RTX in the previous 5 years were analysed. The study examined at demographic and clinical information, as well as the indication for RTX, previous treatments, total rituximab and corticosteroid doses, clinical response, and the presence of side events. Between the first and last clinical examS, the follow-up period was assessed. Complete symptom and analytical remission was regarded complete; partial symptom or analytical response was regarded as incomplete; and no response was regarded if there was no symptom or analytical response.
There were 35 patients (54 % of whom were women, with an average age of 60.1617 years). pSS (31.4%), systemic sclerosis (SS) (17%), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (17%), vasculitis (VS) (20%), necrotizing myopathy (NM) (8.8%), and dermatomyositis (DM) were among the diagnoses (5.8%). Treatment were indicated in 37% of patients, 17% in renal illness, 11.4% in articular symptoms, 14.3% in haematological symptoms, 8.8% in skin involvement, 5.7% in neurologic symptoms, and 5.8% in myopathy. In 80% of the instances, RTX was used after earlier therapies failed, and only 20% of the cases was it used as a first-line treatment. 60% of patients had a full response after receiving rituximab, 17% had a partial response, and 20% were nonresponding. The mean corticosteroid dose was considerably lowered in pSS (p<0.02), 65% in VS (p<0.03), 50% in SS (p<0.04), and NM after rituximab (p<0.046). Infectious problems struck five participants (14%), two of whom required hospitalisation. 7 patients (17%) stopped taking their medication, 5 owing to ineffectiveness (2 SLE, 1 NM, 1 DM, and 1 SS) and 2 owing to infectious problems (14%) (1 pSS and 1 VS). A median of two therapy cycles was completed by the patients. The median follow-up after starting RTX was 48.5 (IQR 25.9-74.4) months.
Concept of D2T RA has now been formalised with the EULAR definition. D2T RA is a heterogenic disease state: one or multiple contributing factors may be present. The patients and economic burden of D2T RA are significant.
Common Issues in Pregnancy Management in Lupus & Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome
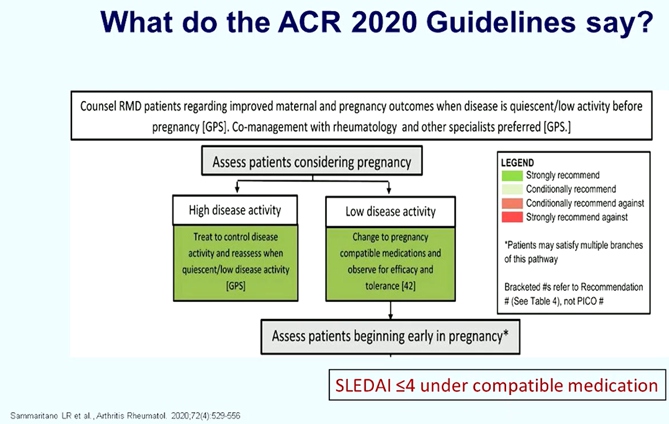
Fischer-Betz R, presented a study in a session at the European congress of rheumatology (EULAR) 2021 scientific sessions: virtual congress. SLE should be still considered severe risk factors for pregnancy. Main risk factors for adverse pregnancy outcomes in SLE such as active disease within 6 months prior to conception, active lupus nephritis, chronic hypertension, pre-exiting renal disease, associated antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, discontinuation of hydroxychloroquine results in pregnancy loss, pre-eclampsia and SLE flares. In the PROMISE study, it was observed that severe flares are infrequent, absent specific risk factors and outcomes are favourable.
Co-management with rheumatology and other specialist preferred [GPS]. Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) should be continued in all patients with SLE. Data suggest that HCQ reduces the risk of pre-eclampsia in lupus pregnancies. Low dose aspirin (75 mg/day -150 mg/day, started 12-16 weeks’ gestation) is recommended for all women with SLE during pregnancy. Pregnancy may be planned in patients with inactive lupus and stable renal function for the preceding 6 months. It is very important to monitor patients for 6-9 months on switched therapy. If possible increase AZA dose to 150 mg/d depending on tolerability. Patients with stable lupus nephritis who switch from MMF to AZA or remain on AZA for pregnancy rarely develop renal flares and have favourable pregnancy out-comes. Rituximab conditionally recommends continuing until conception during pregnancy only in life organ threatening disease. Cyclophosphamide: teratogenic “only in life organ threatening disease in 2nd and 3rd trimesters. In aPL positive patients, the impact of supportive care alone can result in better livebirth rates. On the 14th April 2021, the ENTIS board and scientific committee announced the official position of the ENTIS organization to encourage the use of COVID-19 vaccines in pregnant and lactating women, where the benefits are considered to outweigh the risks.
Recent findings reported common issues in pregnancy management in lupus & antiphospholipid syndrome such as risk of pregnancy in SLE have improved substantially but remain increased vs. healthy women; SLE activity, renal involvement, and aPI are the most important predictors of complications. Recommendations for pregnancy planning and treatment should be implemented as standards in daily practice.
Patients’ Education, Expectations and Outcomes
Zangi HA, presented a study in a session at the European congress of rheumatology (EULAR) 2021 scientific sessions: virtual congress. EULAR recommendation for patient education for people with inflammatory arthritis includes doctors provision of information and patients as passive recipients to patients involvement in decisions and management of their care.
EULAR recommended that communication and shared decision-making is essential and support people in managing their disease. Patient education should be a part of normal care for all people with inflammatory disease, delivered throughout the disease course according to the individual patient’s needs, is provided in individual consultations, online, and as group programmes, delivered by health professionals and trained patients and evaluated by outcome measures reflecting the programme objectives.
It essential to identify questionnaires for evaluation of the aspects such as effective consumer scale (EC-17), arthritis self-efficacy scale (ASES-11), health education impact questionnaire (heiQ) & patients activation measure (PAM). Health literacy helps in knowledge, motivation, social and communication skills that enable people to understand and use health information that enhance health well-being and engagement in medical decision making. Low levels of health literacy leads to difficulty in participating in shared decision making and poorer education adherence and self-management and over all poorer health status. Low levels of health literacy are more prevalent in elderly, people with chronic conditions, low education, low socio-economic status and minority groups.
There is a need for paying attention to health literacy in targeted populations with RMDs, looking at how interventions can be designed to meet expectations and needs from different populations, investigating which content, methods and delivery modalities are best suited to enhance health literacy and how to ensure participation in designing, planning, delivering and evaluation of patient education.
Understanding the Patient Perspective / Patient Expectation on Treatment Outcomes

Boyd P, presented a study in a session at the European congress of rheumatology (EULAR) 2021 scientific sessions: virtual congress. The objective of the study is to understand the patient perspective/ patient expectation on treatment outcomes. The author explains the essential three word phase for both rheumatologist and patient such as listen, understand and care. There have been advances in the technology during lockdown but in the rheumatology flare, it is made listing very difficult. For many people living with this diseases, their appointments are being canceled, delayed or being postponed. The author reported that technology hasn’t help rheumatology for a long time to the same extent. The barrier to better treatment and better communications has shown in various ways: delays in getting appointments, delays in the waiting room to see the consultants and turned the focus of the appointment from the way of patients to the frustrations of not being seeing and listening too.
As patients we want doctors/health care professionals to understand us, to understand that we are in real pain, to understand that we in fatigue. Patients would like doctors to listen- to verbal and non-verbal speech, understand their concerns and difficulties and care about their and their arthritis as well as theirs goals and aim. Patient should listen to the medical experts, understand their restrictions on time and resources and care to ensure the relationship is long and worthwhile. Finally, for now, patients are hoping for care and protect from the healthcare professionals.
Following these straightforward aims will lead to better disease control, disease management and treatment outcomes.
Taking Control–Managing Different Expectations towards Treatment Outcomes: Adherence and Belief
Baraliakos MX, presented a study in a session at the European congress of rheumatology (EULAR) 2021 scientific sessions: virtual congress. The EULAR 2019, GRAPPA 2015 and ACR/NPF 2018 guidelines are available as the treatment recommendation used in psoriatic arthritis. International recommendations and T2T concept strongly recommend treatment based on shared decisions in daily practice. Shared decision and appropriate drug profiles are the factors for treatment adherence. Treatment adherence leads to disease modification and treatment adaptation with good long-term responses. Good long-term responses allow for better patient monitoring.
Patient’s treatment expectation is to set up personal, social, and treatment goals and to monitor disease progress to achieve these goals. Physician treatment expectations includes the main target is ultimately sustained remission, the alternative target is sustained low disease activity and therapy is adapted to promote remission or low disease activity. Patient’s adherence is as important as patient’s satisfaction. Some of the EULAR 2021 recommendations for the implementation of self-management strategies in patients with inflammatory arthritis include: patient education should be the start point and underpin all self-management interventions, HCPs should actively promote physical activity at diagnosis & throughout the disease course, better emotional well-being leads to better self-management; therefore, mental health needs to be assessed periodically and appropriate intervention should be made if necessary and digital healthcare can help patients to self-manage and should be considered for inclusion in supported self-management where appropriate and available.
International recommendations and T2T concept strongly recommend treatment based on shared decisions in daily practice. Shared decisions and appropriate drug profile are the factors for treatment adherence. Treatment adherence leads to disease modification & treatment adaptation with good long-term responses. Good long-term responses allow for better patient monitoring.
Taking Control – Managing Different Expectations towards Treatment Outcomes: Assessing Treatment Failure

Aletaha D, presented a study in a session at the European congress of rheumatology (EULAR) 2021 scientific sessions: virtual congress. Assessing treatment failure in chronic-inflammatory immune mediated diseases is complex and it is only one piece of the management puzzle that we are facing in this type of disease.
The patient may different approaches to what they consider failure success for e.g. they have a strong focus on pain, dependence/loss of work and leisure capacity, more worried about toxicity of therapy and fear today is often bigger than fear for tomorrow. Whereas, Rheumatologist approach is to sees the patient and the disease, fears the disease, considers long-term damage and long-term disability and gear for tomorrow is often bigger than fear of today. Patient empowerment has been part of international recommendations for a quite a while:
- EULAR 2013 – overarching principle A : treatment of RA patients must be based on a shared decision between the patient and the rheumatologist.
- ACR 2015 – the best treatment decisions will be made by clinicians incorporating patient’s values and preferences. A useful tool not only to guide treatment in clinical practice but also facilitate discussions about individualized treatment decision-making between patients & their clinicians.
- APLAR 2013 – Recommendation 2: treatment of RA is a shared decision between clinician and patient and should be started once diagnosed.
In a study it was reported that 1 out of 4 (25%) patients are non-adherent and 71% are intentionally nonadherent over the first 6 months of the treatment.
As a rheumatologist it is essential to understand when patients feel that they might be failing by the therapies because it is as important as there is biological failure.
Mechanisms of Hyperinflammation in COVID-19 and Beyond
Professor Dr. Eugene Feist, presented a study “Mechanisms of hyperinflammation in Covid-19 & beyond” in a session at the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology, (EULAR) 2021.
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) can be differentiated into primary and secondary forms. Secondary HLH (MAS) is well known by rheumatologists but is often underdiagnosed. Hyperinflammation in severe COVID-19 is characterised using cytokine and chemokine release. Risk factors for the evolution of HLH include fever, hepatosplenomegaly, neurologic alterations, and organ infiltration by activated macrophages and hemophagocytes. Post mortem analysis in SARS-CoV2 include heavy congestion and diffusely oedematous lung parenchyma consistent with a clinical diagnosis of ARDS.
Clearance of SARS-CoV2 is uniquely dependent on Type1 INF signalling. Unique pattern of immune dysregulation in severe COVID-19 is characterised by IL6 mediated low HLA-Expression & lymphopenia, NK cell depletion and exhaustion, dysregulated neutrophils, and sustained cytokine production & hyperinflammation. Real world data is especially important because its more diverse, as mortality is linked to elevated LDH, serum ferritin, serum IL-6 levels at hospital admission.
Hyperinflammatory syndrome & MAS contributes to disease severity and mortality in COVID-19. Viral escape and dysregulated host innate immune response contribute to this complication. Cytokine storm is promoted by pyroptosis, activation of pattern recognition receptors, immune cell infiltration and activation (Th1 and M1 polarized response). This could be the basis for therapeutic approaches to modulate and silence the pathologic immune response.
Success and Failures of Therapies for Hyperinflammation in COVID-19
Professor Xavier Mariette, presented a study “Success and failures of therapy for hyper inflammation in Covid19” in a session at the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology, (EULAR) 2021. Aer multivariate analysis adjusted on markers of inflammation hypoxia, other vital signs, demographics and comorbidities, baseline serum levels of IL-6 and TNF-alpha independently predicted disease severity and mortality. Immunomodulatory drugs like corticosteroid, Il-6 inhibitors, IL1i, JAKi, Colchicine are used for COVID-19 therapy.
8 TCZ randomised controlled trials were conducted in COVID-19 patients. 4 met their primary end point, CORIMUNO-19 (ventilation/death), EMPACTA (ventilation/death), REMAP-CAP (Survival) & RECOVERY (survival). The other 4 did not meet their primary end-point, RCT-TCZ-COVID-19 study group (28-day mortality-2.4%), BACC Bay Toc Trial (28-day mortality-4.9%), COVACTA (very heterogeneous inclusion criteria), Coalition COVID-19 Brazil VI (15-day mortality-17% with TCZ and 3% with UC). 1033 hospitalised patients with COVID-19 were included in a randomised study between remdesivir (<10days) and remdesivir with baricitinib (<14days). Primary end point as time to hospital discharge was reported as 8 and 7 days respectively with 28-day mortality of 5.1% and 7.8%. 4488 non- hospitalised patients were included in a trial where randomization between colchicine (0.5mg twice daily for three days and once daily thereafter) or placebo for 30 days was performed. The primary efficacy end point was the composite death or hospitalisation for COVID-19.
Immunomodulators should not be given early in COVID-19 infection. Corticosteroid (dexamethasone 6 to 10mg/day) should be given in patients requiring oxygen, high flow or mechanical ventilation. A recent meta-analysis from WHO demonstrates an efficacy of Toclizumab especially if associated with DXM in patients requiring oxygen. Interest of combinations between immunomodulators and antivirals can be explored in their combination with interferon.
Pediatric Inflammatory Multi System Syndrome
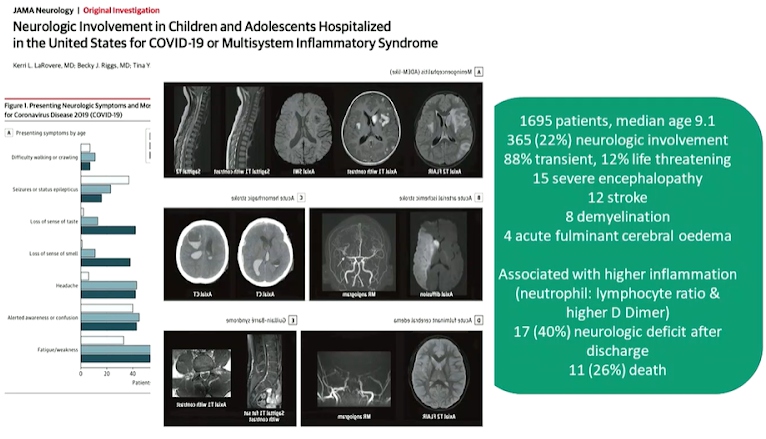
Professor Michael Levin, presented a study “Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) following SARS-CoV-2” in a session at the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology, (EULAR) 2021. MIS-C appears one month behind the COVID-19 peak in populations. Neutrophil damage seems to be prominent in MIS-C. It has higher level of inflammatory cytokines than uncomplicated childhood COVID-19 infection. Children have higher IL17 and INGF levels than adults. MIS-C has a higher immunoglobulin response than COVID-19 and higher IgG1.
Antibody data raises concerns that children with MIS-C have a different antibody response that may play a role in disease either by forming immune complex direct tissue toxicity or activating neutrophils and macrophages. There is a lot to learn about the immunology of MIS-C, clinical findings implicate a pathological role for exoproteome-directed auto antibodies in COVID-19 with diverse impacts on immune functionality and association with clinical outcomes. Paediatricians world-wide faced a new spectrum of disease caused by SARS-CoV-2. Acute COVID mostly mild in children but sever disease in very young, adolescents and those with co-morbidities. MIS-C is a post infectious disorder with a wide spectrum of presentations. Research is needed to understand mechanisms, diagnosis and management.
It is essential to study the biology of these new spectrum of diseases and conduct a detailed clinical phenotyping as well as sample collection. RNA, DNA, serum, plasma, cells, postmortem tissue in acute stage and convalescence will enable us to study the genetics, biomarkers of severity & diagnosis along with immunopathology. It is of the utmost importance to contribute to local studies.
How to Deal with Oligo-Arthritis?
Dr. Ruchir Singh, presented a study “How to deal with oligo-arthritis?” in a session at the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology, (EULAR) 2021.
In November 2013, a 46-year-old Caucasian male referred to the early arthritis clinic with short duration of le knee pain and swelling. Patient history mentioned 10-week insidious onset of le knee pain and swelling, right knee pain, bilateral should pain, EMS 60 minutes, worse with rest, two weeks prior to joint symptom onset- lethargy, sore throat, non-productive cough with no addition features. Past clinical history mentions fatty liver hypertension, childhood femoral ostomies, no history of renal calculi, no familial history of RA, psoriasis or gout, non- smoker, recent alcohol abstinence and has a drug history of paracetamol and diclofenac.
Examination results indicated pain -70, global- 59, EMS-96, Fatigue-76 and physical exam showed BMI- 38, Afebrile, urinalysis negative, general exam NAD, skin and nails NAD. Initial investigation results indicated RF<11. CCP1, ANA negative CRP 48mg/L, uric acid 324, Vitamin D 51.4, WCC 11.8, ALT90, CK 123, Viral screen negative, ASOT titre 200, throat swab- S.dysgalactiaie (group C), X-ray- normal (no erosions), CXR-normal. Condition was diagnosed as unclassified inflammatory arthritis (possibly post infective) managed with naproxen, PPI. 8 weeks later (Jan 2014) the patient described worsening arthralgia, with transient right wrist swelling. On examination, no clinical synovitis was detected, however persistently raised CRP 54 along with no indication of synovitis or tenosynovitis was determined on ultrasound scans of hands. Management was commenced on 15mg OD reducing regime and hydroxychloroquine 200mg BD.
At the 6-month follow-up, clear clinical synovitis involving bilateral writs was indicated. Inflammatory markers were persistently raised CRP 20, ESR 24, ALT and liver screen normal. DAS28 (CRP) 3.62.
In 2021, the patient was diagnosed with recent onset symmetrical small joint arthritis and raised inflammatory markers (ESR 41 and CRP 19).
Eular Recommendations for the Implementation of Self-Management Strategies in Patients with Inflammatory Arthritis
Dr. Elena Nikiphorou, presented a study “EULAR Recommendations for the implementation of self-management strategies in patients with Inflammatory Arthritis” in a session at the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology, (EULAR) 2021.
The key objective was to develop recommendations for implementation of effective self-management strategies facilitated by HCPs in IA concurrently with and complimentary to the delivery of standard medical care which will have tailored care planning and shared decision making at its centre. They aspire to enable all members of the rheumatology MDT to be able to provide a continuous and appropriate measure of support to enable better IA patient self-management and to improve overall patient experience, disease outcomes and quality of life.
- Healthcare professionals should encourage patients to become active partners of the team & make them aware of health care professionals and patient organisations involved in all aspects of the care pathway.
- Patient education should be the start-point and underpin all self-management interventions.
- Self-management interventions that include problem solving and goal setting relevant to the individual and available, cognitive behavioural therapy, should be incorporated into the daily routine clinical practice to support patients.
- Health care professionals should actively promote physical activity at diagnosis and throughout the disease course.
- Lifestyle advice based on evidence should be given to better manage common comorbidity & patients should be guided and encouraged by their health care team to adopt healthy behaviours.
- Better emotional wellbeing leads to better self-management therefore mental health needs to be assessed periodically and appropriate intervention made if necessary.
- Health care professionals should invite discussion with patients about work and sign to sources of help where appropriate or where needed.
- Digital healthcare can help patients to self-manage and should be considered for inclusion in supported self-management where appropriate and available.
- Health care professionals should make themselves aware of available resources to sign-post patients as part of optimising and supporting self-management.
EULAR recommendations are now available for the implementation of self-management strategies in IA. These should be used alongside the medical management guidelines to support patients in their care. A dissemination strategy is currently underway.
The Relationship between different IGG and IGA Anti-Modified Protein Auto Antibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritis
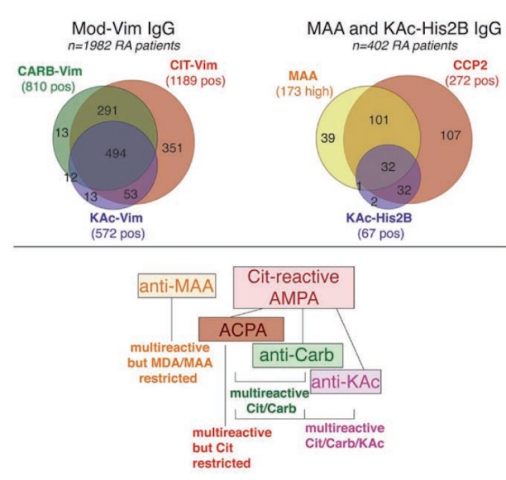
C. Gronwall, presented a study “The relationship between different igg and iga anti-modified protein auto antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis” in a session at the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology, (EULAR) 2021, Scientific program. The reactivity of serum IgG and IgA auto-reactivity to different post-translational modifications in RA was evaluated.
Reactivities of 30 different IgG and IgA AMPA to modified antigens were analysed using ELISA & auto antigen arrays, in n=1985 newly diagnosed RA patients and population controls. Both previously established (i.e IgG and IgA CCP2; IgG ACPA fine-specificities; IgG anti-Carb fibrinogen and Carb FCS; IgG and IgA Cit/Carb/KAc/Orn(Ac)-vimentin), and novel assays (e.g. IgG anti-MAA and IgG anti-acetylated histones) were performed. Additionally, the association of patient characteristics such as smoking and disease activity with autoreactivity was analysed. The efficiency of the novel assay was determined in SLE disease controls and CCP2+ RA-risk individuals without arthritis.
Carb and KAc reactivities were found in patients positive for citrulline-reactivity. When AMPA reactivities were directly compared using modified vimentin (mod-Vim) peptides, patients with high IgG anti-Cit-Vim levels and a history of smoking tested positive for IgA AMPA recognizing mod-Vim. RA specific anti-acetylated histone 2B reactivity was associated with high anti-CCP2 IgG levels, multiple ACPA fine specificities, and smoking. IgG acetylation reactivity was found in a patient who showed positive Cit and Carb reactivity and CCP2+ RA-risk individuals without arthritis. Further, it was confirmed that IgG auto reactivity is not RA specific, and has low correlation with other AMPA. However, highest IgG auto reactivity was observed in CCP2+. IgG autoreactivity to MAA was significantly higher in in RA compared to controls. Anti-MAA was found to be associated with disease activity.
RA patients could be subdivided into four different subsets based on their AMPA, IgG & IgA reactivity profiles. Anti-Carb and anti-KAc could be considered reactivities within the “Citumbrella”, however MAA had distinct reactivity. Multi-ractive β-cell clones could be used to derive autoantibodies exhibiting different patterns of ACPA fine-specificities, Carb and KAc reactivity.

