Changes In Peripheral Nerve Function with Antidiabetic Drugs and Lifestyle in Prediabetes: The ePREDICE European Trial
R. Gabriel
Combination therapy exhibited effectual in the management of early T2D, however, its viability and effectiveness on microvascular complications in the prediabetes is not known yet. R. Gabriel, presented a session at IDF World Diabetes Congress 2025 from 7th-10th April 2025 in Bangkok. The goal of this randomised controlled trial is to compare the possible advantage of adding glucose-lowering drugs, either monotherapy or its combination compared with lifestyle intervention on microvascular parameters (peripheral nerve and kidney function) in prediabetes.
809 of adults aged 45 -74 years with prediabetes (IFG and/or IGT) were enrolled in the multicenter, randomised, controlled trial. Patients were randomized to Metformin monotherapy, Linagliptin monotherapy, its fixed-dose combination or masked placebo. All participants were involved on lifestyle intervention. Outcomes was 1-year change in electrochemical skin conductance (ESC) estimated using SUDOSCAN, and glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
A total of 658 patients (81·3%) of individuals randomised completed the 1-year examination. The fixed-dose combination of Linagliptin/Metformin substantially improved ESC as compared to placebo (-2.1 µS; 95% CI: -4.16; -0.04; p = 0.0458). The fixed-dose combination Linagliptin/Metformin showed substantially higher Kidney function, estimated by eGFR compared with placebo (3.3 mL/min; 95% CI: 0.38; 6.22, p = 0.03). FPG was substantially lower with Metformin monotherapy (-0.3 mmol/L: 95%CI: -0.48; 0.12, p=0.0009), and with the fixed-dose combination Metformin/Linagliptin (-0,2 mmol/L; 95% CI: -0.37; -0.03, p = 0.0219) compared with placebo. Metformin monotherapy (-2.0 kg/year, 95% CI: -5.65; -1.65, p=0.0006) and the combination Metformin/Linagliptin (-1.9 kg/year; 95% CI: -3.02; -0.97 p=0.0002) showed substantially higher reduction in body weight compared with placebo.
1-year management with combined dual therapy with Metformin and Linagliptin in people with prediabetes was uniformly correlated with a better preservation of microvascular peripheral nerve function and kidney function than monotherapy with these drugs or placebo.
Changes In Prevalence of Cardiovascular Risk Factors Between Men and Women in Rural and Urban Southern India
A. Nanditha
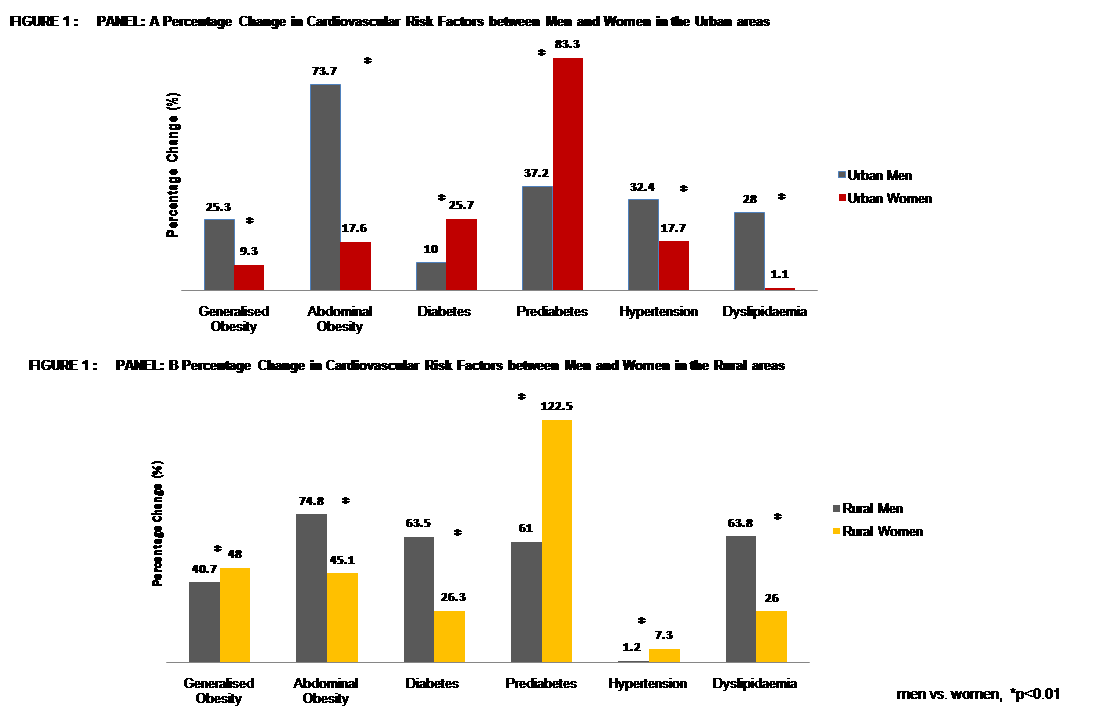
Nanditha A, presented a session at IDF World Diabetes Congress 2025 from 7th-10th April 2025 in Bangkok that evaluated the changes in the cardiovascular risk (CV) profile between men and women in urban and rural locations of Southern India. The percentage change in the prevalence of dysglycaemia and CV risk factors in a 10-year period were compared in this ancillary examination of a large epidemiological survey, STRiDE.
In the urban population, women showed higher percentage increase (PI) in the prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes as compared to men; obesity, hypertension and dyslipidaemia were greater in urban men (Figure 1, Panel A). In the rural areas, men exhibited a greater PI for abdominal obesity, diabetes and dyslipidaemia than women. Prediabetes raised by two-fold (122.5%) in rural women as compared to men. Generalized obesity and hypertension were also higher between rural women as compared to men (Figure 1, Panel B). In both locations, women exhibited substantial enhancement in their physical activity and decreased sedentary time than men. Poisson regression examination exhibited that in urban women, increasing age, abdominal obesity and dyslipidaemia to be correlated with a 39% increase in the prevalence of dysglycaemia.
Urban women exhibited increased prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes in spite of enhanced lifestyle and comparatively low CV risk.
Triple Fixed-Dose Combination of Dapagliflozin + Sitagliptin + Metformin in Managing T2DM
P. Miglani
Fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) with definite procedures and complementary modes of action are effectual in managing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) and aid decrease pill burden and improve patient compliance. Miglani P, presented a session at IDF World Diabetes Congress 2025 from 7th-10th April 2025 in Bangkok that aimed to assess the clinical outcomes of the FDC of Dapagliflozin (10 mg), Sitagliptin (100 mg), and Metformin (500 mg) (DSM) in treating T2DM.
T2DM patients with inadequate glycemic control (HbA1c >7%; Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) >126 mg/dL; post-prandial blood sugar (PPBS) >200 mg/dL) were incorporated in this retrospective study. Patients were initiated on the triple FDC regimen of DSM. Clinical efficacy was evaluated by estimating enhancements in mean difference in HbA1c, FBS, and PPBS parameters at 3 and 6 months respectively. Compliance was calculated by Hill Bone medication adherence scale.
252 participants (Male: Female – 1.4) with a mean age of 58.5±11.4 years were included in the study. Nearly all patients exhibited hypertension (100%) and dyslipidaemia (98.5%). An overall enhancement was shown in glycemic parameters, with substantial mean reductions in HbA1c (-2.2±1.4%; P<0.05), FBS (-56.2±26.8; P<0.05), and PPBS (111.3±72.8; P<0.05) gained by the end of the study period (6 months) irrespective of duration of T2DM. At the end of the study, target HbA1c (<7%), FBS (<100mg/dL) and PPBS (<140mg/dL) was acquired in 80%, 41.3% and 21% of individuals respectively. The occurrence of genitourinary tract infections was comparable among baseline (n=6) and post-treatment (n=9). A mean weight loss of 5.9kg was seen. 95.2% and 98% of individuals showed good medication compliance (80-100% compliance) at 3rd and 6th month respectively.
The FDC of DSM effectually accomplishes glycemic control in patients with T2DM without increasing the occurrence of genitourinary tract infections. The effect of the modest weight loss requires to be assessed in addition with longitudinal studies.
Incidence of Microvascular Complications in Young-Onset Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes in India-Results from the ICMR-YDR
N. Tandon
There is a lack of comprehensive data on the incidence of diabetic complications in individuals diagnosed with young-onset type 1 (T1D) and type 2 (T2D) diabetes. Tandon N, presented a session at IDF World Diabetes Congress 2025 from 7th-10th April 2025 in Bangkok that assessed the occurrence of microvascular complications in Indian individuals with young onset T1D and T2D.
The incidence of retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy was evaluated across a follow-up period of 19 years (2001 to 2020) in individuals diagnosed with T1D and T2D enlisted in ICMR- Young Diabetes Registry (YDR). The incidence of complications was estimated in those > 10 years in age and disease duration > 5 years in individuals with T1D, and in all individuals with T2D. Diabetic retinopathy was examined with an ophthalmoscopic dilated fundus analysis executed by an ophthalmologist. Diabetic nephropathy was diagnosed if 24-hour urine protein or albumin excretion overreached 500 mg and 300 mg respectively. Diabetic neuropathy was assessed by clinical analysis and the monofilament test.
In the YDR, 21,728 individuals with young onset diabetes, (65.3 % T1D (N=14,194), 24.0% T2D (N=5218) were enlisted. The age adjusted incidence of retinopathy was 31.7 /1000 person years (CI: 27.4-36.7) in T1DM and 25.0 /1000 person years (CI 20.5-30.5) in T2D; neuropathy, 15.3 (CI 12.5-18.6) and 24.2 (CI 19.8-29.6); and nephropathy, 12.2 (CI 9.8-15.3) and 18.0 (CI 14.5-22.4) in T1D and T2D, respectively (Table 1).
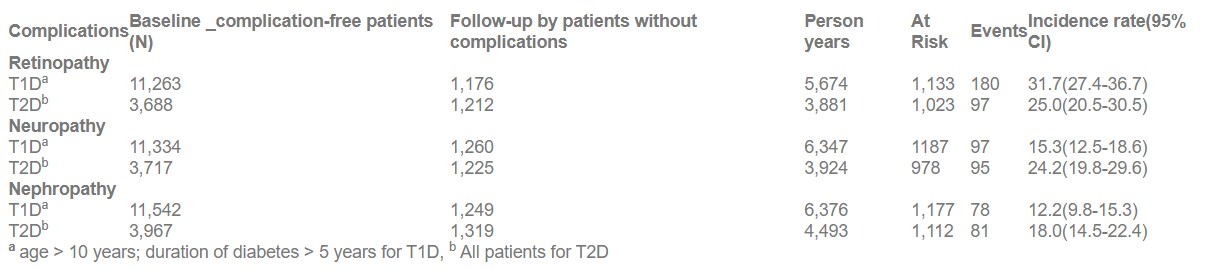
Young-onset T2D patients in India showed a greater incidence of microvascular complications particularly neuropathy and nephropathy than T1D.
Preferences for SGLT2 vs. DPP4 Inhibitors in Asian patients with T2DM: A Multicentre Cross-Sectional Study
M. Tiwaskar
Sodium-Glucose Co-transporter-2 Inhibitors (SGLT2I) and DipeptidylPeptidase-4 Inhibitors (DPP4I) are emerging treatments (tx), offering effective glycemic control without increasing the risk of hypoglycemia. Considering patients’ (pts) preference is crucial to ensure tx adherence. Tiwaskar M, presented a session at IDF World Diabetes Congress 2025 from 7th-10th April 2025 in Bangkok that evaluated pts tx preference for T2DM in Asian countries between medication profiles resembling SGLT2I (medication A) and DPP4I (medication B).
The cross-sectional study (Nov 2021-Nov 2022) adult T2DM patients across India, Philippines and Taiwan, completed a survey to identify their preferred medication profile. Descriptive statistics and Chi-squared/Fisher’s exact tests were employed to detect differences in pts baseline characteristics and choice between the two profiles across three regions. The study included 1224 pts (Philippines-34.8%, India-32.7%, Taiwan-32.5%), with a mean age of 59.3 years. Philippines had highest proportion of females (64.8%) and greater prevalence of hypertension (73.7%) and dyslipidemia (81.2%) vs India (46.5%, 58.3%,59.3%) and Taiwan (45.2%, 55.5%, 76.9%).
Compared to Philippines and Taiwan, India had high proportion of overweight/obese pts (64.8%) and pts with uncontrolled glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c, 70.8% vs. 53.3% [Philippines] and 48.7% [Taiwan], p<.001); but low prevalence of chronic kidney disease (8.5%) and dyslipidemia (60.3%). Philippines showed lowest use of biguanides (74.6%) compared to India (90.3%) and Taiwan (87.4%); while India reported high use of sulfonylureas ([73.5% vs 26.8%: Philippines and 36.2%: Taiwan). SGLT2I was significantly preferred over DPP4I (64.5% vs 35.5%; p<0.001) with Philippines reporting highest preference (80%), followed by Taiwan (58%) and India (54.5%).
Among Asian patients with T2DM, SGLT2 inhibitors were preferred over DPP4 inhibitors. Understanding patient preferences and the factors influencing treatment choices can help improve adherence and clinical outcomes.
Age-Specific Patterns of Obesity and Sleep Quality in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
S. Patil
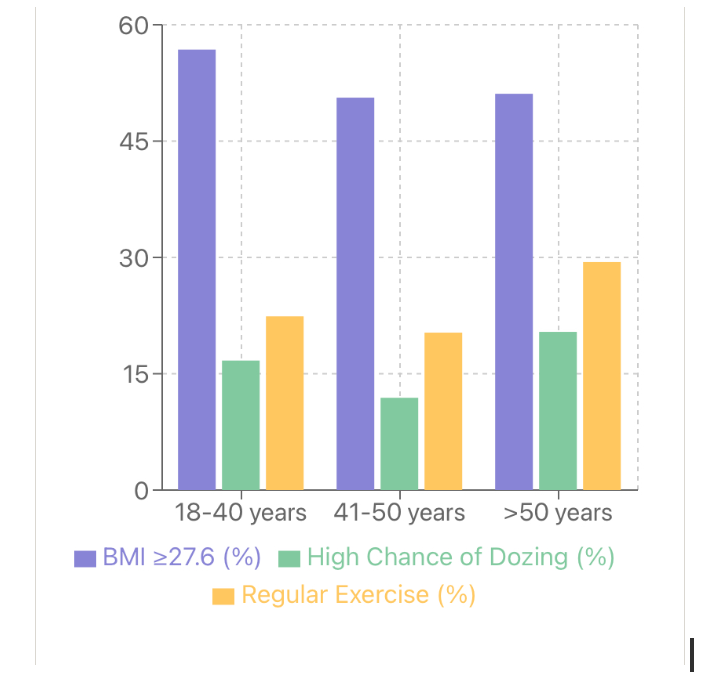
The interplay between obesity, sleep quality, and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) is complex, particularly in newly diagnosed patients. Understanding age-specific patterns can inform targeted interventions. Patil S, presented a session at IDF World Diabetes Congress 2025 from 7th-10th April 2025 in Bangkok that analyzed age-specific relationships between obesity markers, sleep quality, and glycemic control in newly diagnosed T2DM patients.
A cross-sectional study of 591 newly diagnosed T2DM patients was conducted. Patients were stratified into three age groups: 18-40, 41-50, and >50 years. BMI, Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) scores, HbA1c levels, and lifestyle factors were analyzed. Chi-squared tests and one-way ANOVA were used for analysis. Younger patients (18-40 years) showed the highest prevalence of obesity (56.8% with BMI ≥27.6 kg/m²), compared to 50.6% in 41-50 years and 51.1% in >50 years groups. Poor sleep quality (high chance of dozing in ESS) was most prevalent in the >50 years group (20.4%), compared to 16.7% in 18-40 years and 11.9% in 41-50 years groups. Mean HbA1c levels were similar across age groups (9.4%, 9.2%, 9.4% respectively). Regular exercise (>150 min/week) was most common in the >50 years group (29.4%) compared to younger groups (22.4% and 20.3%). High BMI (≥27.6 kg/m²) was significantly associated with higher ESS.
The findings revealed distinct age-specific patterns in obesity and sleep quality among newly diagnosed T2DM patients. Younger patients show higher obesity prevalence, while older patients report poorer sleep quality but more regular exercise. The consistent association between high BMI and poor sleep quality across all ages highlights the need for tailored management strategies addressing both factors in early T2DM care.
The Impact of Sedentary Lifestyle Choices and Breakfast Skipping on Plasma Glucose Levels in Indian T2D Patients
M. Bera
Type 2 diabetes and obesity may result from the widespread practice of skipping breakfast. There was no decrease in 24-hour energy expenditure in earlier investigations that imposed a single incidence of skipping breakfast. Bera M, presented a session at IDF World Diabetes Congress 2025 from 7th-10th April 2025 in Bangkok, that evaluated how sedentary behaviour and skipping breakfast for six days in a row affected glycemic control and energy metabolism.
Using a repeated-measures strategy, ten young men were divided in two groups (with or without breakfast) that lasted six days in a row. The continuous glucose monitoring equipment was used to measure each subject’s blood glucose levels during the meal intervention. Subjects who skipped breakfast consumed substantial meals for lunch and dinner and without breakfast group also having extremely sedentary lifestyle as they spent entire day by sitting in a single room. Fasting (142.8 ± 31.6 mg/dl vs 108 ± 19.71 mg/dl, P = 0.008), peak post-lunch (221.8 ± 26.2 mg/dl vs 168.6 ± 34.65 mg/dl, P < 0.001), and HOMA-IR (3.06 ± 3.74 vs 2.05 ± 1.68, P = 0.007) were substantially greater for those who skipped breakfast. Although the BS visit saw higher fasting serum insulin levels, the difference was not statistically significant (7.45 ± 5.10 mIU/ml during BE vs. 9.15 ± 12.55 mIU/ml during BS, P = 0.059). During breakfast skipping, CGM showed a greater post-lunch AUC0-180. Glycemic variability, TIR, ABG, and post-dinner AUC0-180 did not differ. Glycemic variability, TIR, ABG, and post-dinner AUC0-180 did not differ.
In Indians, skipping breakfast may result in a larger post-lunch glucose excursion due to a rise in glucagon and insulin resistance (IR) rather than incretin-mediated insulin production.
Multi-Protein Signatures Associated with Insulin Sensitivity and Secretion in Youth: Insights from the PANTHER Study
Y.J. Choi
Comprehending the cause and development of youth-onset type 2 diabetes (T2D) requires an understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying impaired insulin sensitivity and secretion throughout puberty.
Choi YJ, presented a session at IDF World Diabetes Congress 2025 from 7th-10th April 2025 in Bangkok, outlining a study designed to determine proteins linked to insulin sensitivity and secretion in pubertal children through proteomic analysis and minimal model (MINMOD) assessment of intravenous glucose tolerance tests (IVGTT).
Of the 91 children (ages 8-15 years) in the PANTHER research, 43% were obese (BMI ≥ 95th percentile) and 11% had Type 2 Diabetes. Acute insulin response to glucose (AIRg), β-cell function, disposition index (DI), and insulin sensitivity (SI) from IVGTTs using MINMOD. Partial Spearman correlations between proteins and each MINMOD output were conducted, controlling for diabetes status, BMI, and HbA1c.
There were positive correlations (r=0.38, 0.36, 0.33) between AIRg and cathepsin H (lysosomal enzyme), coagulation factor IX (blood clotting), and NAG (involved in inflammation). Negative associations were found between HLA-A2 (immune response) and AOC1 (polyamine metabolism) (r=-0.43, -0.35). WISP2 (cell growth) and myostatin (muscle growth inhibitor) were positively correlated with β-cell function (r=0.35, 0.33), while H6ST3 (heparan sulfate synthesis) and MIA (melanoma marker) were negatively correlated (r=-0.41, -0.39). DI had a negative correlation (r=-0.27, -0.25) with IL-31 (cytokine) and STC1 (calcium/phosphate homeostasis), and a positive correlation (r=0.29, 0.25) with ALDH12A1 (aldehyde metabolism) and UBD (ubiquitin protein). SI had a positive correlation (r=0.41, 0.39) with CMC4 (cation transporter) and glypican 3 (cell proliferation), and a negative correlation (r=-0.46, -0.40) with UCK2 (pyrimidine metabolism) and coagulation factor IX.
The study provided information on insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction by identifying proteins correlated with insulin sensitivity and secretion throughout puberty. These findings could direct future therapies to delay or prevent T2D in young people.
Efficacy and safety of Dapagliflozin vs Sitagliptin for type 2 DM in Geriatric population: A Randomized Control Trial
R.R. Mohanty
Worldwide, the geriatric diabetic population is estimated to reach 276.2 million by 2045. DPP4 inhibitors and SGLT2 are currently the most significant medications in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the geriatric population, following metformin. There have been very few studies evaluating the efficacy and safety of Sitagliptin vs Dapagliflozin in the elderly population. So, we conducted this study.
Mohanty RR, presented a session at IDF World Diabetes Congress 2025 from 7th-10th April 2025 in Bangkok, where the objective was to assess and compare the change in HbA1c levels, renal parameters, lipid profiles, and the occurrence of all significant adverse events from baseline at 12 weeks in both groups.
A parallel group with an open label randomized control trial was carried out among people with diabetes who were over 60 years and had insufficient glycemic control. Two groups of 120 patients were randomly assigned to receive either Sitagliptin 100 mg once daily or Dapagliflozin 10 mg once daily as add-on treatment for three months. From baseline to 12 weeks, the following were examined: baseline demographic details, changes in HbA1c, fasting blood sugar, two hour post prandial blood sugar, fasting lipid profile, serum creatinine, glomerular filtration rate, urea, and incidence of adverse events.
The paired t test revealed a substantial reduction in HbA1c levels at 12 weeks in both groups Sitagliptin [8.30±0.74 to 7.49±0.61% (0.84±0.34, 95% CI 0.74 to 0.93), p value of <0.001] and Dapagliflozin [8.05±0.81 to 7.35±0.71 (0.64±0.39, 95% CI 0.54,0.74) p value <0.001]. An Independent sample Mann Whitney U test showed that Sitagliptin outperformed Dapagliflozin in terms of HbA1c reduction (p-value <0.001)
Compared to the Dapagliflozin group, the Sitagliptin group has a statistically significant change in FBS, PPBS, Total cholesterol, LDL, and Serum urea. There was no statistically significant difference in HDL, Serum creatinine, glomerular filtration rate, or the occurrence of adverse events.
Sitagliptin and Dapagliflozin were both similarly safe and effective in the management of diabetes in the Geriatric population, according to this RCT.
The Impact of Screen Time on Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients – The SCREEN Study
A. Karuppan
Adults’ screen time continues to be a source of concern due to its impact on health habits and clinical outcomes. The relationship between screen time and glycemic parameters in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is poorly understood. Understanding the influence of screen time on lifestyle changes and glycemic control is critical for managing T2DM in addition to medication. Karuppan A, presented a session at IDF World Diabetes Congress 2025 from 7th-10thApril 2025 in Bangkok, aimed at assessing the effects of a multidisciplinary counselling intervention on screen time behaviour and how it affects adults with T2DM ability to control their blood sugar levels.
This interventional study comprised 300 T2DM patients through a convenience sampling method, who supplied data regarding their Screentime (Screentime Questionnaire) using a previously validated 18-item questionnaire. A multidisciplinary team counselled participants about the impact of screen time on glycemic management.
We found a significant link (rho = 0.178, P = 0.002) between HbA1c levels and weekday screentime (including and excluding work hours), as well as weeknight and weekend screen times. FBS and PPBS also had a favorable correlation with screentime. 217 individuals returned for a follow-up 3 months after the intervention. The educational intervention resulted in a statistically significant decrease in HbA1c from 7.47 ± 1.53 % to 7.21 ± 1.46% (p <0 .001), with a mean difference of 0.27 ± 1.17% and a mean screentime reduction of 0.61 hours.
Our findings revealed a strong link between increased screentime and poor glycemic management among Indian T2DM adults. This is supported further by a drop in HbA1c levels by 0.27% in 3 months following an educational intervention. As screen time increases, the impact on sedentary behaviour becomes increasingly obvious. Understanding how it affects glycemic control in individuals with type 2 diabetes is crucial for improving non-pharmacological treatment methods.

