Obesity affects over one billion people globally, driving chronic disease burden. Orforglipron, an investigational oral glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, offers a potential non-injectable treatment for weight management. The Phase 3 ATTAIN-1 trial evaluated its efficacy and safety in adults with obesity or overweight with weight-related comorbidities, excluding diabetes.
ATTAIN-1 (NCT05869903), a 72-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, enrolled 3,127 participants across multiple countries with BMI ≥30 kg/m² or ≥27 kg/m² with comorbidities (e.g., hypertension, dyslipidemia). Participants received orforglipron (6 mg, 12 mg, or 36 mg) or placebo once daily, alongside diet and exercise counseling. Primary endpoint was percent body weight reduction at 72 weeks (efficacy estimand). Secondary endpoints included proportions achieving ≥10% and ≥15% weight loss and cardiovascular risk marker changes. Safety was assessed via adverse event monitoring.
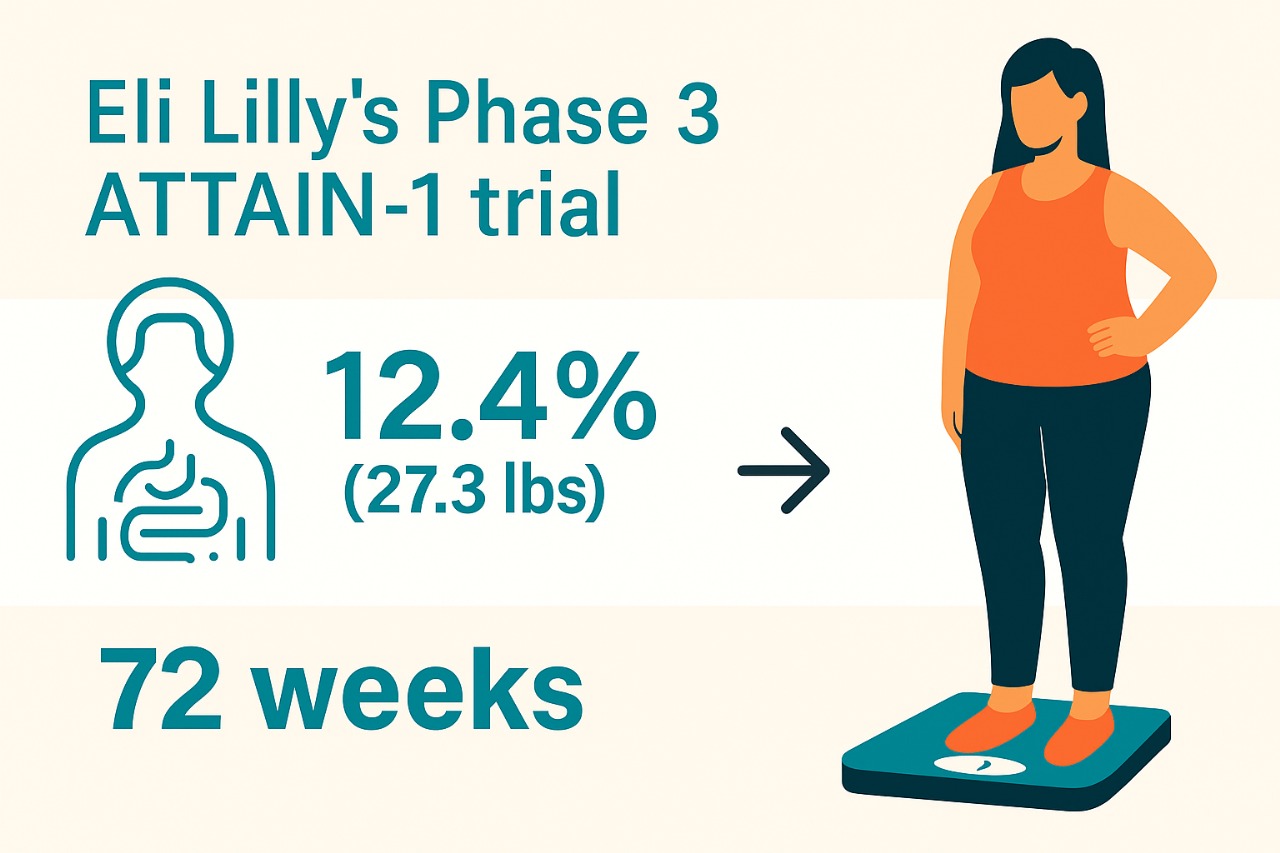
Orforglipron 36 mg achieved a mean 12.4% (27.3 lbs) weight reduction from a baseline of 103.2 kg, versus 0.9% (2.2 lbs) for placebo (p<0.05). Lower doses yielded 7.8% (6 mg) and 9.3% (12 mg) reductions. For 36 mg, 59.6% and 39.6% of participants achieved ≥10% and ≥15% weight loss, respectively, compared to 8.6% and 3.6% for placebo. Treatment-regimen estimand results showed 11.2% (36 mg), 8.4% (12 mg), and 7.5% (6 mg) reductions versus 2.1% for placebo. Orforglipron reduced non-HDL cholesterol, triglycerides, systolic blood pressure, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (47.7% at 36 mg). Common adverse events were gastrointestinal (nausea: 33.7%, constipation: 25.4%, diarrhea: 23.1% at 36 mg), mostly mild-to-moderate, with 10.3% discontinuation due to adverse events (vs. 2.6% placebo). No hepatic safety signals were observed.
Orforglipron demonstrated clinically meaningful weight loss and cardiovascular risk improvements, positioning it as a promising oral therapy for obesity. Its safety profile aligns with GLP-1 agonists, with manageable gastrointestinal effects. Lilly plans regulatory submission by 2025, with further ATTAIN and ACHIEVE trial data forthcoming.

