Dapagliflozin, a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, has shown potential in improving metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) without worsening liver fibrosis, according to findings published on June 4 in The BMJ.
The multicenter, double-blind, randomized trial conducted across six tertiary hospitals in China involved 154 adults with biopsy-confirmed MASH. Participants were randomly assigned to receive either 10 mg of dapagliflozin or a placebo once daily for 48 weeks. The primary endpoint was improvement in MASH — defined as a reduction of ≥2 points in the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score (NAS) or achieving a NAS ≤3 — without worsening fibrosis.
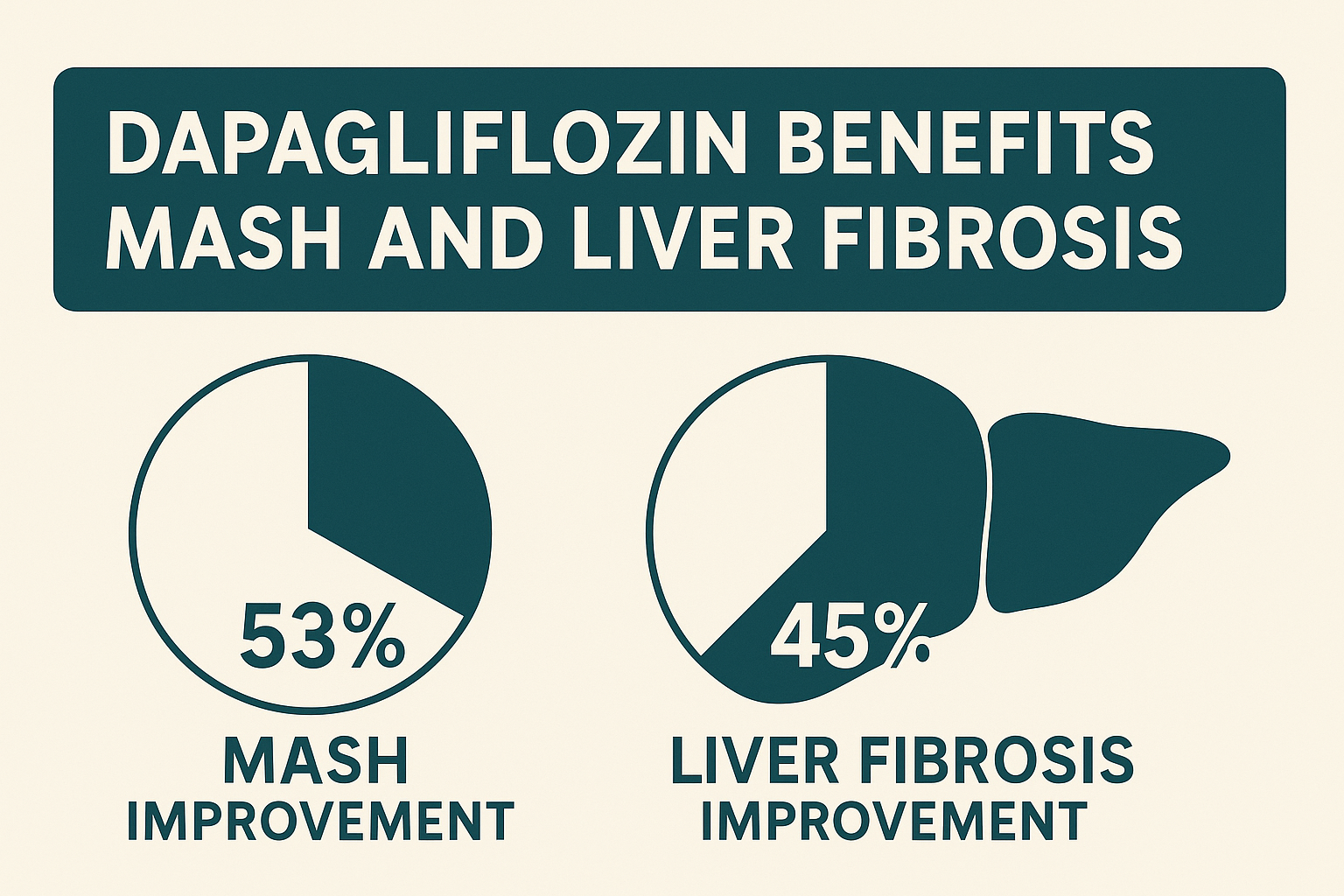
Results showed that 53% of patients in the dapagliflozin group achieved MASH improvement without fibrosis worsening, compared to 30% in the placebo group. This translates to a risk ratio of 1.73, with a mean NAS reduction of −1.39. Moreover, MASH resolution without fibrosis worsening occurred in 23% of the dapagliflozin group versus 8% in the placebo group (risk ratio, 2.91).
Importantly, the drug also demonstrated benefits for fibrosis. Fibrosis improvement without worsening of MASH was seen in 45% of the dapagliflozin group, significantly higher than the 20% observed in the placebo group (risk ratio, 2.25). Adverse event-related discontinuation was minimal, occurring in only 1% of the dapagliflozin group and 3% of the placebo group.
Lead researcher Jiayang Lin from Nanfang Hospital of Southern Medical University and colleagues highlighted the dual benefit observed with dapagliflozin — both in resolving liver inflammation and improving fibrosis — a rare achievement in MASH therapeutics.
The findings reinforce the potential of dapagliflozin as a safe and effective treatment for patients with MASH, offering hope in a field where therapeutic options remain limited. Larger, long-term studies are needed to validate these promising results and explore the broader applicability of dapagliflozin in liver disease management.

