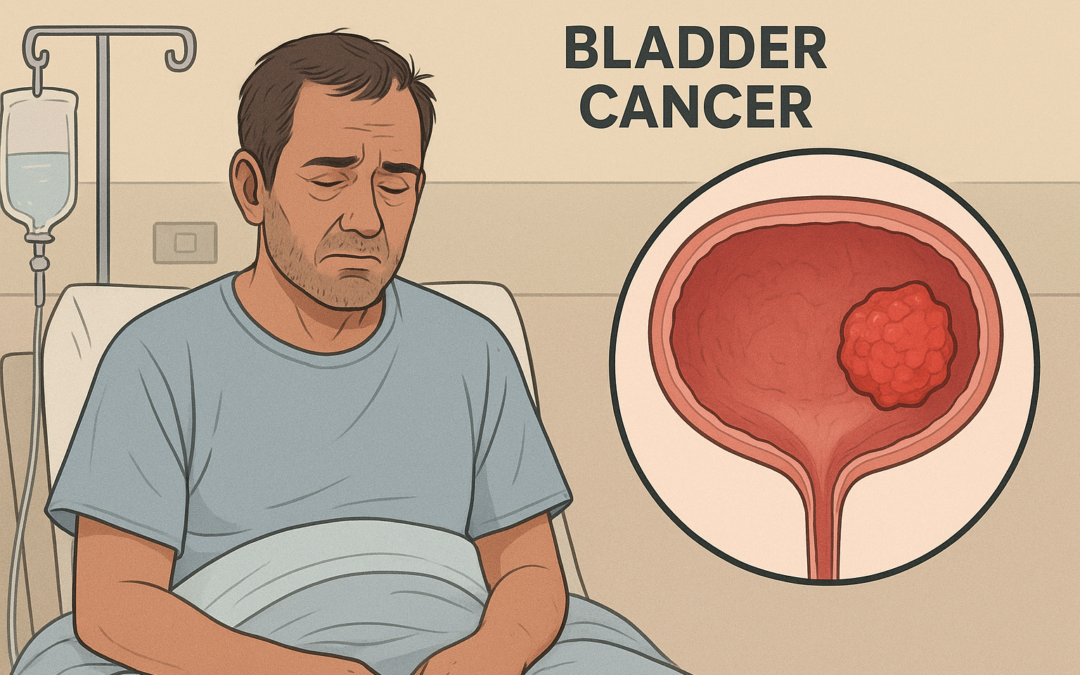
Johnson & Johnson’s Innovative Medicine division marked a significant advancement in oncology on September 9, 2025, with the U.S. FDA approval of INLEXZO™ (gemcitabine intravesical system), formerly known as TAR-200. This novel therapy targets adult patients with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG)-unresponsive non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) characterized by carcinoma in situ (CIS), with or without papillary tumors—conditions affecting about 10% of NMIBC cases and leaving patients with few bladder-sparing alternatives post-BCG failure. INLEXZO™ addresses a critical unmet need in a field stagnant for over four decades, offering a potential paradigm shift by enabling extended local chemotherapy delivery without the morbidity of radical cystectomy, which carries a 3-8% postoperative mortality risk and profoundly impacts quality of life, particularly among older patients.
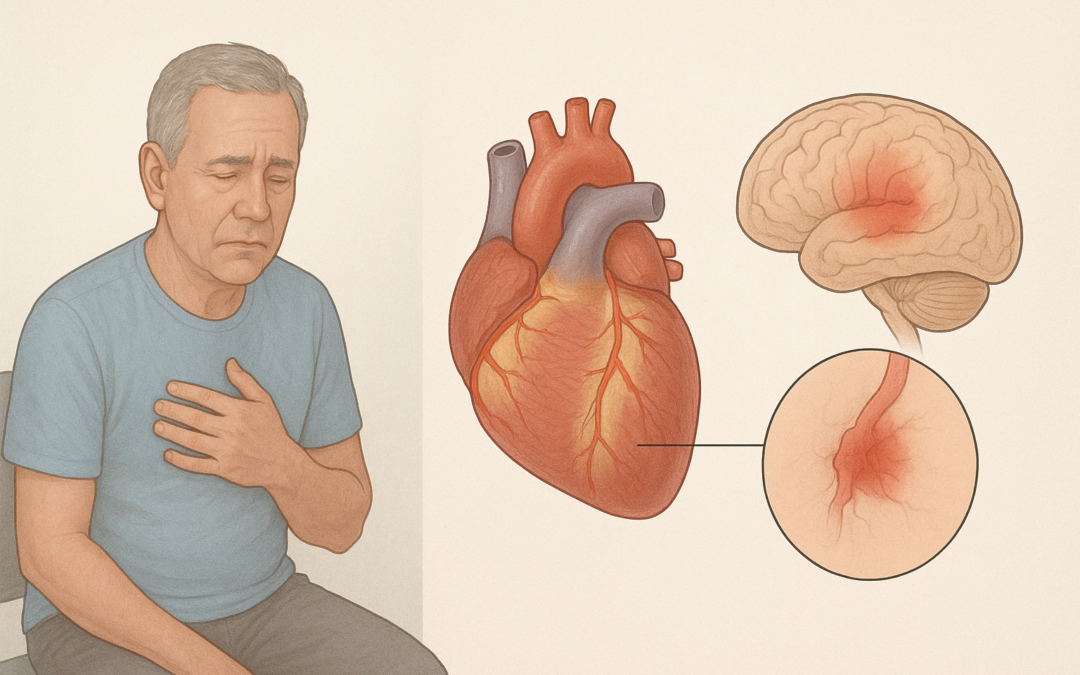
This secondary analysis of the ARCADIA trial, a randomized study comparing apixaban versus aspirin for secondary stroke prevention in patients with cryptogenic stroke and atrial cardiopathy, investigated the relationship between left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction and recurrent ischemic stroke, as well as the efficacy of apixaban in this context.
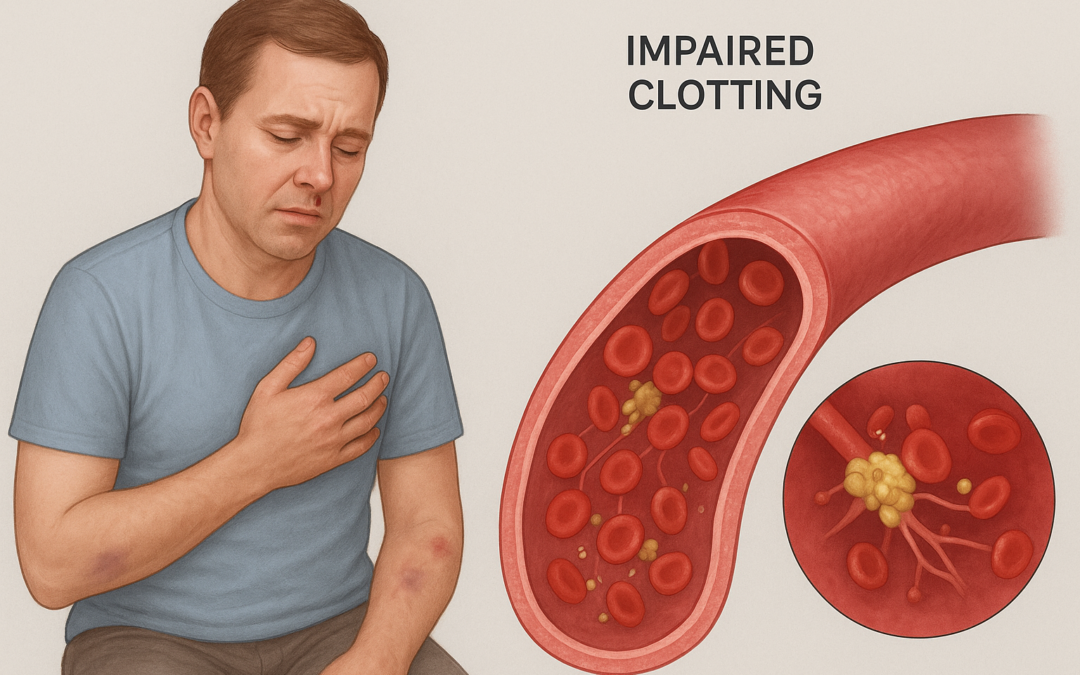
On September 5, 2025, Takeda announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the supplemental Biologics License Application (sBLA) for VONVENDI® [von Willebrand factor (Recombinant)], expanding its indications to include routine prophylaxis for reducing bleeding episode frequency in adults with von Willebrand Disease (VWD), including Type 1 and 2, and on-demand and perioperative bleeding management in pediatric patients.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by amyloid-beta (Aβ) accumulation, including toxic protofibrils, driving cognitive decline in patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or mild dementia. Maintenance therapy is critical to sustain clinical benefits after initial treatment, yet accessible options are limited. Lecanemab, a monoclonal antibody targeting Aβ aggregates, has shown efficacy in slowing AD progression, but IV administration poses logistical challenges. The objective is to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and usability of LEQEMBI IQLIK (lecanemab-irmb), a subcutaneous autoinjector for weekly maintenance dosing in early AD, following 18 months of IV initiation therapy.
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) represents a significant clinical challenge, particularly among patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes, where cardiometabolic factors exacerbate disease progression. While glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists like semaglutide and dual GLP-1/glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) agonists like tirzepatide have demonstrated symptomatic improvements in preliminary trials, evidence on hard clinical endpoints such as hospitalization and mortality remains limited due to small event numbers. The objective of this study is to assess the real-world effectiveness and safety of semaglutide and tirzepatide in reducing heart failure hospitalization or all-cause mortality in patients with cardiometabolic HFpEF, including trial emulation and head-to-head comparisons.






