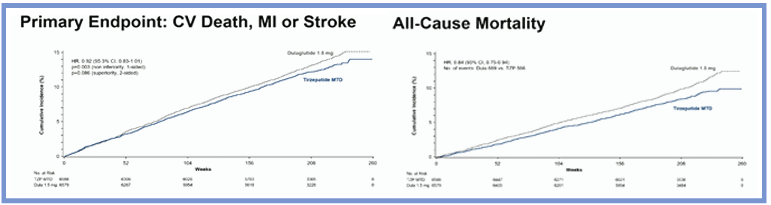
Tirzepatide, a dual GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonist, has been shown to improve glycaemic control and promote weight loss when compared with selective GLP-1 receptor agonists. Benefits of tirzepatide have also been observed for atherogenic lipoproteins, blood pressure, high sensitivity C-reactive protein and kidney function in comparison with selective GLP-1 receptor agonists or basal insulins. Stephen Nicholls assessed the cardiovascular outcomes in participants on tirzepatide versus dulaglutide in the SURPASS-CVOT trial. The findings were presented at the EASD Annual Meeting 2025, held th st from 15- 19 September 2025 in Vienna, Austria.
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a leading cause of heart failure (HF), with left ventricular reverse remodeling (LVRR) linked to better outcomes, including reduced hospitalizations and mortality. While guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) promotes LVRR in HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), the role of ivabradine—a selective If-channel inhibitor recommended for HFrEF patients in sinus rhythm with resting heart rate (HR) ≥75 bpm despite GDMT—remains underexplored in relation to achieved HR and LVRR. This retrospective study at Severance Hospital (2012-2021) analyzed 255 patients with idiopathic non-ischemic DCM (NIDCM), defined by LVEF ≤35% and dilated left ventricle (LV), excluding ischemic, valvular, or other secondary etiologies via comprehensive diagnostics including cardiac MRI.
Eli Lilly and Company announced on September 25, 2025, that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Inluriyo (imlunestrant), a 200 mg oral tablet, for the treatment of adults with estrogen receptor-positive (ER+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2-), ESR1-mutated advanced or metastatic breast cancer (MBC). This approval targets patients whose disease has progressed following at least one line of endocrine therapy (ET), addressing a critical need as approximately 50% of ER+, HER2- MBC patients develop ESR1 mutations after aromatase inhibitor exposure, leading to treatment resistance.
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) poses a major threat to patients with type 2 diabetes, even without prior events. While aspirin is recommended for primary prevention in high-risk diabetic individuals, its benefits are offset by increased bleeding risks, particularly gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. Clopidogrel, a P2Y12 inhibitor, has shown fewer GI events in secondary prevention trials, but its role in primary prevention remains unclear. This study aimed to compare the effectiveness and safety of clopidogrel versus aspirin in high- and very high-risk diabetic patients without ASCVD, using real-world data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service–National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC) from 2010-2019.
Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) is a significant health issue, with sacubitril/valsartan (an angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor) improving outcomes but potentially causing hyperkalemia due to aldosterone suppression and interactions with other therapies. This study evaluated potassium levels and hyperkalemia prevalence in HFrEF patients post-initiation, comparing pre- and post-treatment rates in a real-world Saudi cohort to inform monitoring strategies.






