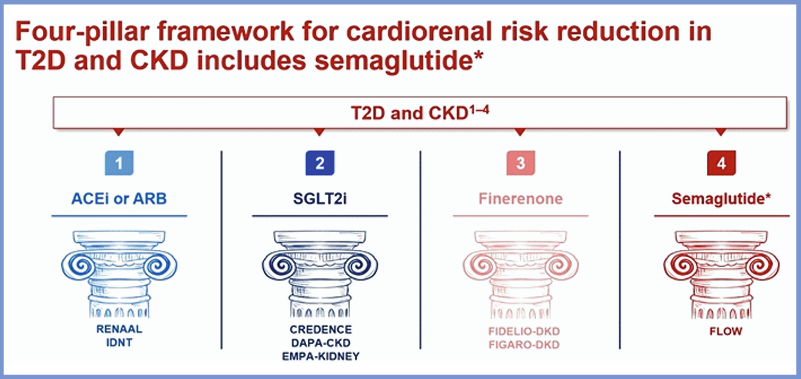
Diabetes is the leading cause of CKD and kidney failure. ~40% of people with T2D develop CKD. The risk of CV mortality increases with increased CKD staging, regardless of diabetes status. Paola Fioretto assessed the role of GLP-1RAs in the CKD and T2D nexus. The findings were presented at the th st EASD Annual Meeting 2025, held from 15-19 September 2025 in Vienna, Austria
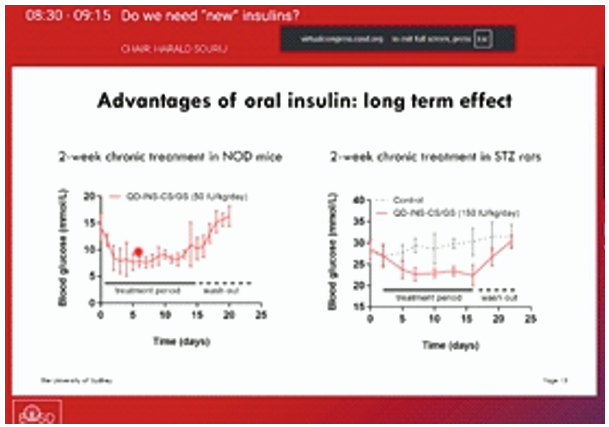
Insulin is highly sensitive to degradation from stomach acid and enzymes, but quantum dot (QD) conjugation can help make it insoluble across a wider pH range. While QD-insulin conjugation improved stability, QD-insulin alone was not effective in mice studies. The findings were presented at the EASD Annual Meeting 2025, held from 15 -19 September 2025 in Vienna, Austria.
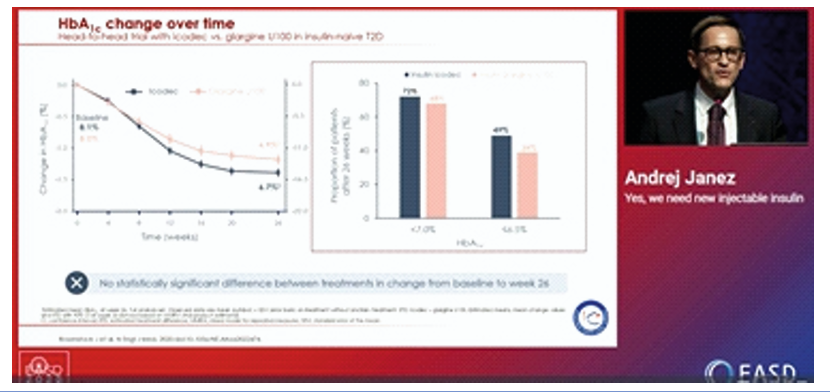
Insulin is the oldest of the currently available diabetes medications, has the most clinical experience. It is the most effective agent when used in adequate doses to decrease any level of HbA1c to the therapeutic goal. The updated ADA/EASD consensus recommends the use of GLP-1 receptor agonists or SGLT2 inhibitors with proven cardiovascular benefit in patients with type 2 diabetes and established ASCVD or high cardiovascular risk. Several studies have stated that initiation of insulin therapy is often delayed, leading to an increased risk of complications in patients with diabetes. The findings were presented at the EASD
Annual Meeting 2025, held from 15 -19 September 2025 in Vienna, Austria.

The REALIZE Study, a retrospective observational analysis, assessed the effectiveness and safety of early initiation of a fixed-dose combination (FDC) of dapagliflozin (SGLT-2 inhibitor) and sitagliptin (DPP-4 inhibitor) in 250 Indian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) across five centers. Eligible patients, aged 18-59 years with a BMI ≥25 kg/m² and HbA1c between 7.0% and 10.5%, were prescribed the FDC for 112 ± 20 days.
Amgen announced on October 2, 2025, that the Phase 3 VESALIUS-CV trial successfully met its dual primary endpoints, establishing Repatha (evolocumab) as the first PCSK9 inhibitor to significantly reduce cardiovascular events in primary prevention settings. This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study enrolled over 12,000 adults at high cardiovascular risk, including those with known atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or high-risk diabetes, but without prior myocardial infarction (MI) or stroke. Participants had elevated lipid levels (LDL-C ≥90 mg/dL, non-HDL-C ≥120 mg/dL, or apolipoprotein B ≥80 mg/dL) despite optimized lipid-lowering therapy, with approximately 85% on high- or moderate-intensity LDL-C reducing regimens like statins.






